Results
This section displays the results of our systematic study of the design and contextual parameters that can influence the power output of a tidal current turbine.
The results presented are shown in terms of the variation in power coefficient, or CP over a range of tidal velocities. CP can be thought of as a measure of the effectiveness of the turbine. It is a non-dimensional coefficient equal to the power extracted by the turbine divided by the power available to the turbine. CP varies with tip speed ratio, and for a fixed rotational speed machine this equates to variation with inflow velocity.
If the power flowing through an area, A, is:
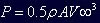
where P is the power in Watts, ρ is the fluid density in kg/m3, A is the area in m2 and V∞ is the flow velocity, then the power extracted from the flow by a turbine with a swept area of ‘A’m2 is:
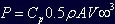
Elsewhere power is generally given in kilowatts (kW) and energy is presented in terms of megawatt hours (MWhrs). In domestic use kilowatt hours (kWhrs) are commonly used but due to the magnitude of the numbers involves it is more appropriate to make use of a unit 1000 times larger.





