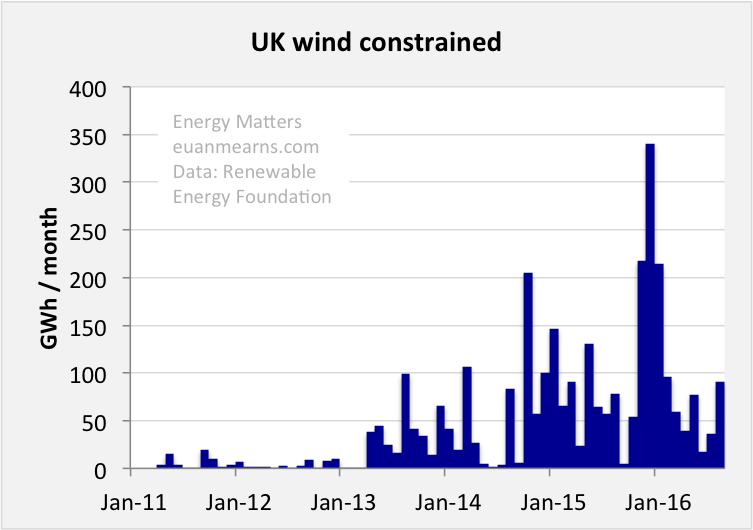
What is Curtailed Wind?
Curtailed wind is when the energy production of a windfarm is reduced, when there is energy that could otherwise be harvested. Wind energy is unpredictable, there are many monitoring and measuring techniques utilise to predict the power output but these cannot be 100% accurate due to the stochastic nature of the wind resource. When wind energy output is inaccurately predicted in forecasting the supply of electricity to the grid may not match demand, this is what leads to wind energy being curtailed.
Curtailment payments were introduced in 2010 however, the money spent on curtailed wind has increased substantially over the past 8 years in correlation with the number of wind farms being commissioned.
Key Factors
There are a number of factors that influence the quantity of wind energy that is curtailed.
- Location
- Grid infrastructure
- Wind speed
- Demand
- Storage capability
Impacts of Curtailed Wind
Financial Impacts
The use of storage can minimise the negative impacts of curtailing wind energy with a reduction of fossil fuel energy production, allowing excess renewable energy to be stored for periods of high demand when renewable penetration is high.
- Curtailment payments are made when wind energy is in surplus and unrequired.
- Public perception - turbines being under utilised will potentially negatively influence individuals perception of their worth and effectiveness.
- Greater landmass allocated for a "power plant" that is not used.
- Gas and coal power plants are much more dispatchable than wind and therefore more reliable when supply is uncertain.
- Low power outputs of wind energy may increase nuclear power plant developments.
- Curtailed wind alters the capacity factor of a wind farm, capacity factor indicates the actual output against potential max output. Therefore during periods of curtailment the capacity factor does not represent the windfarms performance accurately.
The use of storage can minimise the negative impacts of curtailing wind energy with a reduction of fossil fuel energy production, allowing excess renewable energy to be stored for periods of high demand when renewable penetration is high.
Background header: https://wallhere.com/en/wallpaper/773722
[1] http://euanmearns.com/uk-wind-constraint-payments/
[2] http://www.ref.org.uk/energy-data/notes-on-wind-farm-constraint-payments
[1] http://euanmearns.com/uk-wind-constraint-payments/
[2] http://www.ref.org.uk/energy-data/notes-on-wind-farm-constraint-payments