
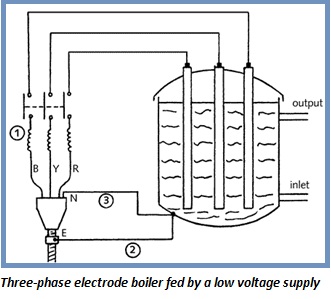
Electrode boilers operate by passing current through the water to generate either hot water or steam. Two or three electrodes are immersed in the water and a single- or three-phase supply is connected to them. The supplying current can only be AC otherwise electrolysis will occur. Water treatment is also essential but only lower quality chemical are required. Their efficiency is nearly 100% with minimal radiation losses.
Electrode boilers have a quick delivery time which makes them ideal for intermittent power supply such as that of renewable sources. No emissions of products of combustion are involved so their carbon footprint is low and they are compact and come in a variety of sizes. Their minimal components and control equipment result to reduced maintenance cost and better reliability. Their operating costs vary according to the energy charges and the energy demand.
References:
- Bard Skagestad, Peter Mildenstein. District Heating and Cooling Connection Handbook. Programme of Research, Development and Demonstration on District Heating and Cooling. International Energy Agency.
- Electric Boilers. (2012). Obtained from http://www.electric-boilers.org.uk/