






Advantages
 Twisted jackets have few joints to produces, which allows saving on costs but it makes the sections heavier as well.
Twisted jackets have few joints to produces, which allows saving on costs but it makes the sections heavier as well.
Disadvantages
 Twisted jackets require twisted piling.
Twisted jackets require twisted piling.
 They require a centre pile-driver that must be vertical while the jacket sits over it.
They require a centre pile-driver that must be vertical while the jacket sits over it.
 They use no less steel than other types of jacket.
They use no less steel than other types of jacket.
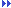 They have not been proven for OWT foundation.
They have not been proven for OWT foundation.
Advantages
 Hexa-base jacket cuts the cost of steel by up to 40% according to weight. (WINDPOWEROFFSHORE, 2013).
Hexa-base jacket cuts the cost of steel by up to 40% according to weight. (WINDPOWEROFFSHORE, 2013).
Disadvantages
 It is more complicated to build than other types of jackets and its manufacture may require more operations, thus increasing the costs.
It is more complicated to build than other types of jackets and its manufacture may require more operations, thus increasing the costs.
 It has six piles which mean six piling operations with their respective piling noise and environmental impact.
It has six piles which mean six piling operations with their respective piling noise and environmental impact.
 They use no less steel than other types of jacket.
They use no less steel than other types of jacket.
 They have not been proven for OWT foundation.
They have not been proven for OWT foundation.

 Four-legged jacket is a proven technology used in the wind industry and can withstand the conditions in locations with 35 m of water depth and beyond.
Four-legged jacket is a proven technology used in the wind industry and can withstand the conditions in locations with 35 m of water depth and beyond.
 They are easier to manufacture than twisted and hexa-base jackets and hence their cost of manufacture is lower if compared.
They are easier to manufacture than twisted and hexa-base jackets and hence their cost of manufacture is lower if compared.
 If one leg fails it does not mean the collapse of the structure which could happen in case of a three-legged jacket.
If one leg fails it does not mean the collapse of the structure which could happen in case of a three-legged jacket.
Disadvantages
 It has an extra leg compared to three-legged jackets so it is 33% more expensive regarding set-up time and piling.
It has an extra leg compared to three-legged jackets so it is 33% more expensive regarding set-up time and piling.
 The extra pile means an extra piling operation with its respective noise and environmental impact.
The extra pile means an extra piling operation with its respective noise and environmental impact.

However there is a concern about if the one leg fails, the three-legged jacket becomes very unstable. This fear comes from oil and gas industry where the consequences of this kind of failure were very important. It can be argued that in the wind industry the consequences would not be as important and therefore the industry should focus on finding solution to this problem and make use of the advantages of three-legged piles.
Advantages
 Three-legged jackets have fewer joints to make and they are easier to produce so their manufacture cost is lower.
Three-legged jackets have fewer joints to make and they are easier to produce so their manufacture cost is lower.
 The amount of steel used is reduced and so are the material costs.
The amount of steel used is reduced and so are the material costs.
 They have fewer piles to drive into the seabed so that the noise and the environmental impact associated with piling operations is minimised.
They have fewer piles to drive into the seabed so that the noise and the environmental impact associated with piling operations is minimised.
 They hold the level better than four-legged jackets.
They hold the level better than four-legged jackets.
Disadvantages
 In case of one leg failure the jacket substructure becomes highly unstable and could bring the structure to collapse.
In case of one leg failure the jacket substructure becomes highly unstable and could bring the structure to collapse.