Methodology for a Decision Support Tool for a Tidal Stream Device
MSc Sustainable Engineering: Offshore Renewable Energy


Techno-Economic Analysis Tool
This tool performs a techno-economic analysis and obtains the approximated Levelised Cost of Energy [LCoE] for the different optimum blades obtained in the Genetic Algorithm of the Blade Element Momentum (BEM) Tool.
Download: Techno-Economic Analysis Tool (Aluminium Input from BEM)
The tool uses the inputs from the Material, Geometric and Economic Properties and combines them with proportional bibliographic relations that approximate the material, manufacturing and logistic costs of the construction and operation of a Tidal Stream device.
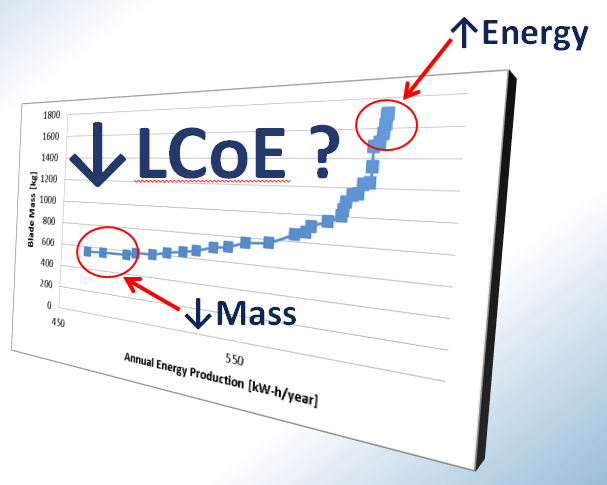
Mass vs Energy balance
Inputs
In this section the Inputs of the Tool are presented:
Material Properties
• Material
o Aluminium Alloy (7075-T6)
o GFRP Laminate (Glass)
o Stainless Steel, Austenitic 304
o CFRP Laminate (Graphite)
• Cost [£/kg]
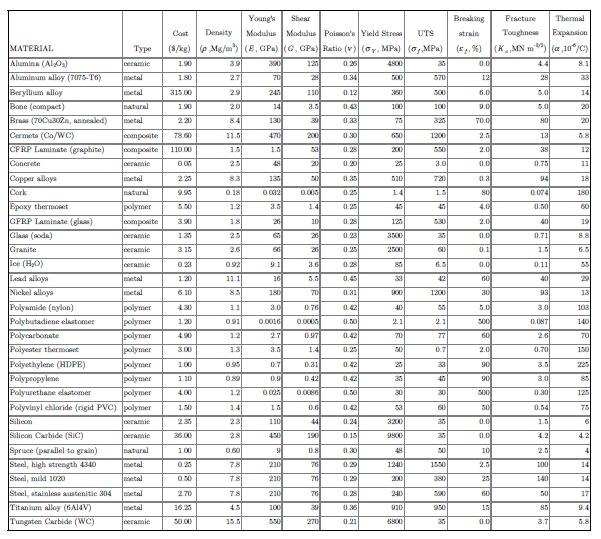
Material Costs [MIT]
Geometric Properties
• Diameter [m]
• Rated Power [kW]
• Availability [%]
• Efficiency [%]
Economic Properties
• CfD Tariff [£/MW-h]
• Discount Rate [%]
Control Properties
• Material/Blade Cost @₤2.35,4000kg [%]
• Blade/Structure&Control Cost [%]
• Structure&Control/Total Cost [%]
• CAPEX/Total Cost [%]
• OPEX/Total Cost [%]
• Decommisioning/Total Cost [%]
BEM Outputs
• Data of 45 blades obtained in BEM Analysis (in the 45 Worksheets of the Excel file)
• Annual Energy Output [MW-h/year]
• Total Blade Mass [kg]
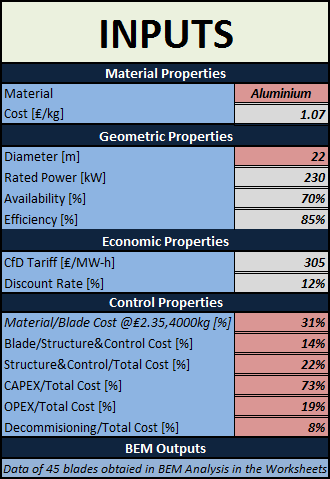
Inputs of the Tool
Outputs
The outputs from the tool are the following:
Efficiency Properties
• Annual Energy Production [MW-h/year] GFRP Laminate (Glass)
• Capacity Factor [%]
Economic Properties
• LCoE [₤/MW-h]
• CAPEX [₤]
• Revenues/Year [₤]
• Discounted Profit Year 20 [₤]
• Payback [Years]
• Project Life [Years]
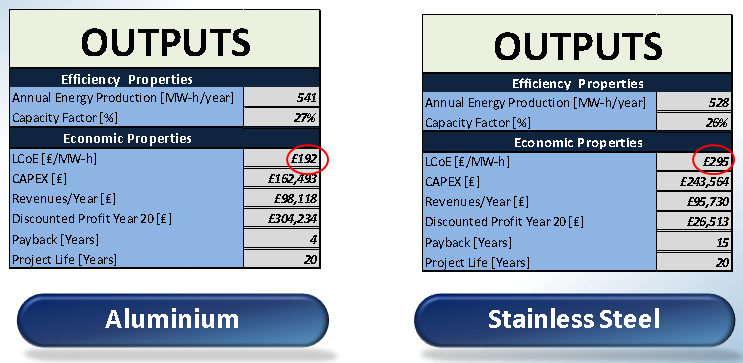
Outputs of the Tool
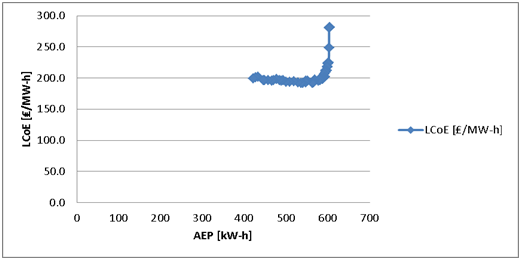
Annual Energy Production vs Levelized Cost of Energy
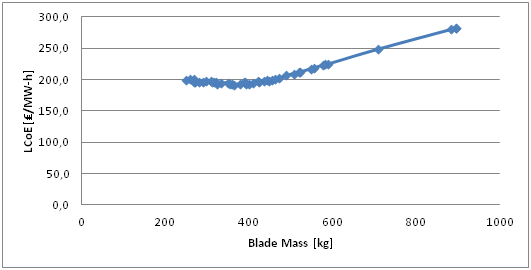
Blade Mass vs Levelized Cost of Energy
Methodology
From “Cost Study for Large Wind Turbine Blades: WindPACT Blade System Design Studies” (TPI Composites Inc):
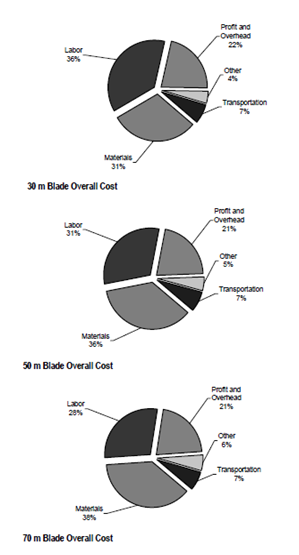
Cost for different Blade Lengths [31]
The data is extrapolated and a theoretical curve is generated to estimate the percentage of the materials cost of the blade relative to the total cost of having the blade installed (through a sensitivity analysis that takes into account the total mass of the blade since it affects the percentages).
Additionally, from: “Issues and Opportunities for Advancing Technology, Expanding Renewable Generation and Reducing Emissions”:
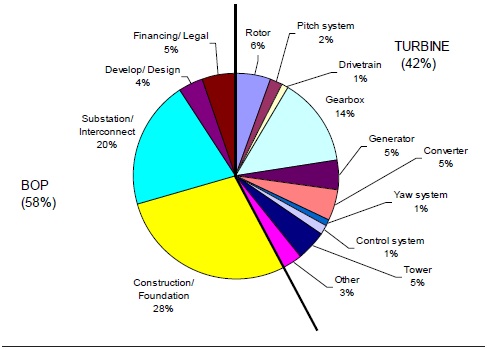
Capital Cost Components [32]
The approximate CAPEX, OPEX and Decommissioning Cost is obtained.
Additionally, the a Discount Rate is used in the calculations as a way to accurately valuing the project using the concept of time value of money, by estimating future cash flow to their present values.
Following recommendations from the Carbon Trust, a Discount Rate of 12% is used in the calculations.
References:
➙ [31] TPI Composites Inc: Cost Study for Large Wind Turbine Blades: WindPACT Blade System Design Studies. May
2013.
➙ [32] EPRI: Issues and Opportunities for Advancing Technology, Expanding Renewable Generation and Reducing
Emissions. July 2011.
➙ [33] Carruthers, Barry; Veguillas, Roberto - ScottishPower Renewables Developing a Business in Marine
Renewables. ICOE Dubin. 2012.
➙ [34] Ricci, Pierpaolo - Tecnalia Mathematical modelling and analysis in Marine Renewable Energy.