PV Case Study
Overview
This case study has been chosen to analyze an existing housing estate and determine its suitability for the integration of solar panels in the roofs of the residential area.
The first process is the selection of the site where the study needs to be carried out. The site can be viewed using Google Earth as shown inthe image to the right.
There are a total of 48 houses in the case study, with the houses being both single and double storey. The demand will vary depending on this data and also the kind of heat and electricity system, gas boilers are the system selected for this case study.
PV panels do not present social restrictions hence the location of the panels is only affected by the maximum efficiency that can be obtained from them. The panels used in the calculations are 100W Poly (MERIT). These panels have High Quality Polycrystalline structure with a peak power of 100W and electricity generated at 12V. The selection of this kind of panels has been influenced by the low price and easy installation.
Along with Google Earth, an online mapping tool and the MERIT and HEM Tools will be used to determine the housing heating demand and the related PV solar capacity. These tools can be downloaded from the Solar Workflow Tab in the Workflow page of this site. Go to PV Workflow
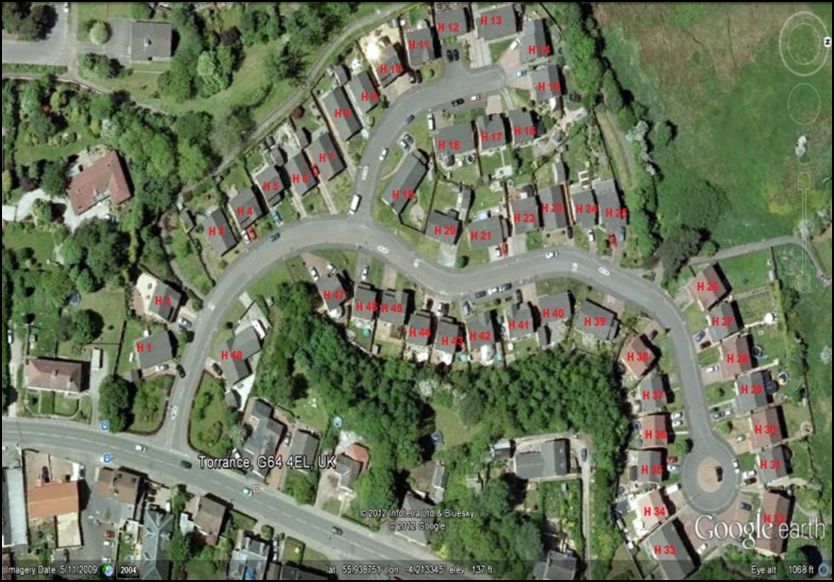

Shown above is a Google Earth image of the housing estate chosen for the PV case study.
Technical Feasibility
Using Google Earth, the orientation angle of each roof was determined. For the calculation of the roof area available for the installation of the panels only roof situated between South East and South West orientations were considered. The areas meeting this requirement were calculated using the tool detailed in the workflow section of this website. An example of the too, being used to determine the rood area is shown below.

The total number of panels implemented in the case study was 402, considering the installation of the maximum number of panels per viable roof. No obstruction or shading roof areas were observed (using Google Street View).
The inclination for the roof was considered as 30° (as per this information source), although variations for this angle can be introduce in the software of calculations MERIT.
The demand model was created with HEM. Of the total number of houses (48) with gas boilers:
- 30 are double storey
- 18 are single storey
The demand for this kind of houses is 29.3 KWh /m² per year and a total electrical demand of 201.116,5 KWh /year is required for this residential area.
The supply/demand analysis is carried out with MERIT as shown in the image below. An iterative process is developed for the calculation of the supply and match profiles. Considering the small variation in energy output between South East and South West orientation, only South orientation is considered for this calculation. Different ranges of demands per house are selected and these are combined with different number of panels varying between 5 and 12 panels per house. Results for energy output and match are included in the spreadsheet 1 and 2.The total energy generated by the panels is 292.8 MW per year and the match is 114.1 MW.

It should be noted that some utility companies directly considered the half of that which is generated is used in the house and the other half is consumed in which case only the actual generation need be known for the tariff calculations (as per this information source).
Financial Feasibility
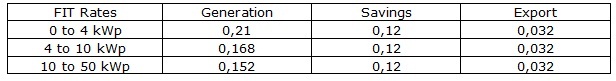
The current tariff for electricity imported from the grid is 12p/KWh and the exported price is 3p/kWh (as per current FIT tariff).
According to the values obtained for the match, the most interesting situation is that with represents a maximum match. This is detailed in the table shown below.
© University of Strathclyde