[Standby Electricity]
Many appliances these days are actually using electricity when they are switched 'off'. This is more commonly known as standby power, where the appliance consumes energy when it is in on standby or OFF mode. These "standby loads" occur in most appliances that use electricity, such as VCRs, televisions, stereos, computers, and kitchen appliances. These appliances continue to draw a small amount of power when they are switched "off".
Although we know we can't switch off fridges and freezers, unless we want to defrost then, it is important to switch off appliances once they have been finished with. To avoid the standby mode and help stop wasting money we need to change the way we behave. Hopefully the following sections will help demonstrate the problem and illustrate where changes could be made and how much money the homeowner could save. A significant amount of energy can be saved across Scotland by reducing the electricity demand being wasted by electrical appliances in the standby mode.
The problem of standby power consumption is essentially a technological concern; more should be done by the appliance industry to help reduce the power consumption by equipment in standby mode. However, switching the appliance off at the correct place, or unplugging the appliance can help avoid paying for standby electricity. Alternatively using a multi-socket power bar can make it easier to turn off several appliances at once.
Kitchen, Bedroom, Bathroom, Living room.
Household Standby Electricity Consumption
Many people are perhaps unaware that appliances on 'standby' actually consuming electricity needlessly. By switching off appliances at the wall we can actually save money and also the environment by reducing carbon dioxide emissions.
Taking the examples from the living room, kitchen, bedroom and bathroom, which have been illustrated above the total saving can be demonstrated over the period of a year. This illustrates a wide variety of possible electricity being consumed unnecessarily and the thought of paying for electricity that we are not using is not a nice one, especially when it could be costing £116 per year - worst case scenario.
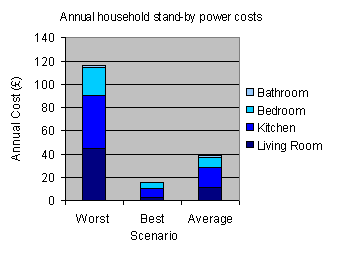
In most probability standby electricity is more likely to cost somewhere in the region of £38.
The idea of paying for something that we are not using is not very encouraging. Consider switching appliances of properly in a bid to safe electricity, this is not only saving you money but also helping the environment. If you want to find out how much money you could save by reducing standby electricity consumption in your own house please try the Standby Electricity Consumption Guide.
From our calculations the current average household standby power consumption as 60W, however this amount could increase further with the growing number of electronic appliances in the average house.
60W = 0.060 kW x 8760 hrs = 525.6 kWh / year
Taking the average household electricity consumption
as 3,880 kWh per year this indicates that standby power is responsible for
13% of home power consumption. The associated costs for a three bedroom flat
are estimated at £35.70
For detailed analyses follow the links below
![]()
Home, Urban, Cutting
the cost, Kitchen, Bathroom,
Bedroom, Living room,
Consumption Guide Instructions
![]()