ESP-r: Summery of Simulation Entities
The data model is embedded within the source code of ESP-r. Header files define parameters determining the size of the data structures. There are alternative header files to support smaller models and/or constrained computing platforms, medium scale models as well as larger projects.
The evolution of the data model also tends to involve changes to model files (see below) as well as the source code. With few exceptions data structures are documented within the source code, primarily where they are read from file or within the source header files.
In general, older model files (up to roughly a decade old) can be read and used with little or no user intervention. There are facilities to upgrade model files, usually with little or no user intervention.
The ESP-r data model is a super-set of that used by conventional CAD tools. It also includes visual entities used by Radiance, acoustic attributes, life-cycle attributes, as well as unused optical attributes from imports of optical data. Each entity has a set of attributes and supports a specific set of thermophysical interactions.
The following types of entities are included:
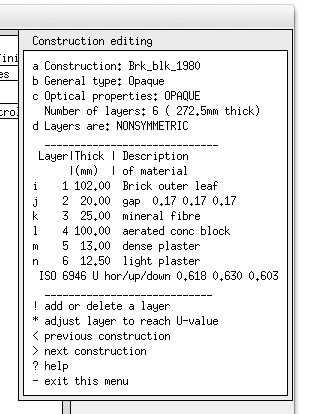
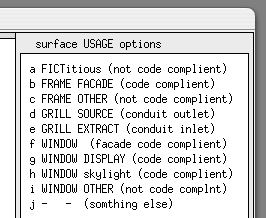

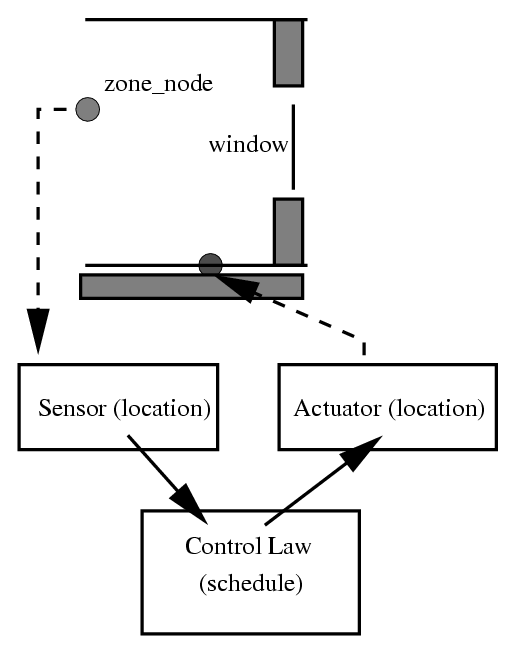
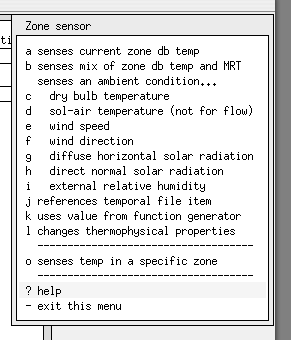
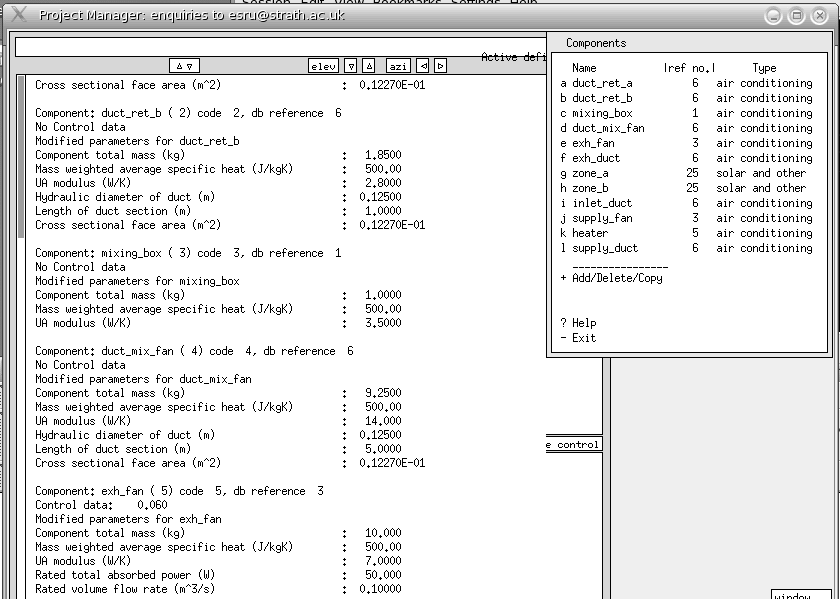
As components are selected for use the user updates the component attributes for the specifics of the network in the model. The user then specifies the nodes in associated sending components to complete the network description.
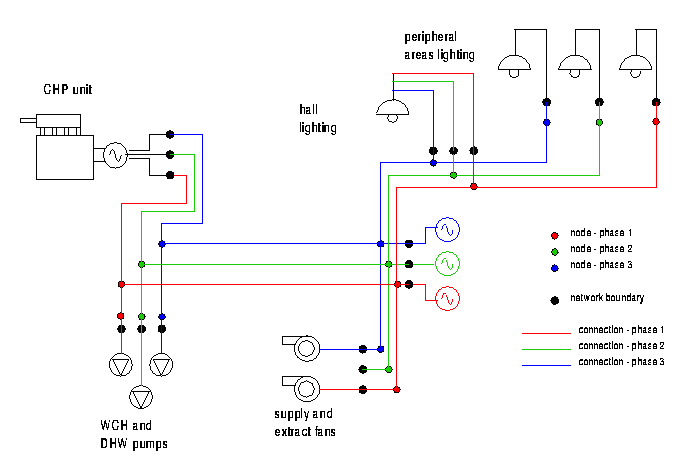
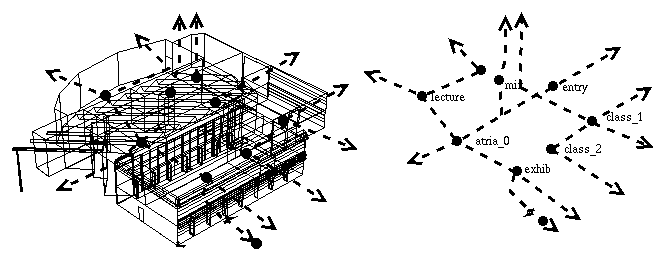
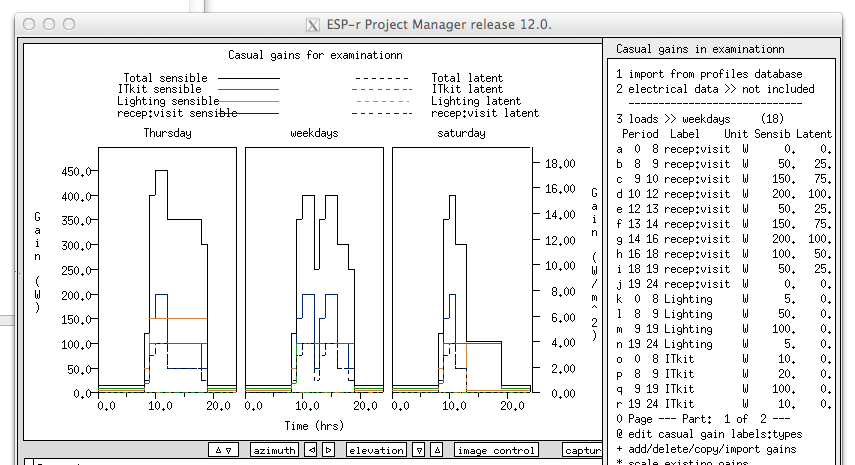
Summery of model files
ESP-r models are held in a distributed folder structure with different entity types in different files (see below).
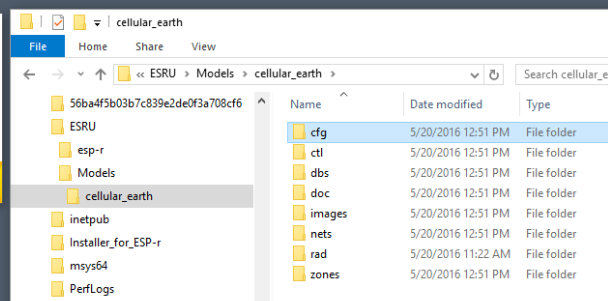
Inside each of the folders are topic-specific model files. Below are the files for one of the simple exemplar models. The functionality-follows-description of ESP-r created new files as the user evolves a model. File name extensions give a clue as to the topic. In the case below an explicit zonal representation of an earth tempering conduit has resulted in additional files - .htc are heat transfer coefficient directives for those zones.
cellular_earth
--- cfg
--- cellular_earth.cfg - the model cfg file
--- cellular_earth.cnn - the master list of surface boundary conditions
--- ctl
--- cellular_earth.ctl - environmental control definitions
--- dbs
--- multicon.db5 - model-specific construction database
--- doc
--- cellular_earth.log - user notes about the model
--- cellular_earth_db5.contents - the QA report about the model
--- images - images associated with the model
--- earth_tube.fig
--- earth_tube.gif
--- earth_tube_temp_mod.gif
--- layout_of_earth_tube.gif
--- spring_earth_tube_perf.gif
--- summer_earth_tube_cool.gif
--- nets - network definition folder
--- cellular_earth.afn - mass flow network
--- rad - Radiance files (none for this model)
zones
--- corridor.con - thermophysical properties
--- corridor.geo - geometry and attribution
--- corridor.opr - casual gains & scheduled infiltration
--- corridor.tmc - optical properties
--- manager.con
--- manager.geo
--- manager.obs
--- manager.opr
--- manager_a.con
--- manager_a.geo
--- manager_a.obs
--- manager_a.tmc
--- manager_b.con
--- manager_b.geo
--- manager_b.opr
--- manager_b.tmc
--- tube_a.con
--- tube_a.geo
--- tube_a.htc - heat transfer coefficients
--- tube_a.opr
--- tube_b.con
--- tube_b.geo
--- tube_b.htc - heat transfer coefficients
--- tube_b.opr
--- tube_c.con
--- tube_c.geo
--- tube_c.htc - heat transfer coefficients
Most model files are ASCII text and follow a tag:data format (a few files include position-specific formatting).
FILE EXAMPLES TO BE ADDED HERE
Back to top | Back to Welcome page