Application
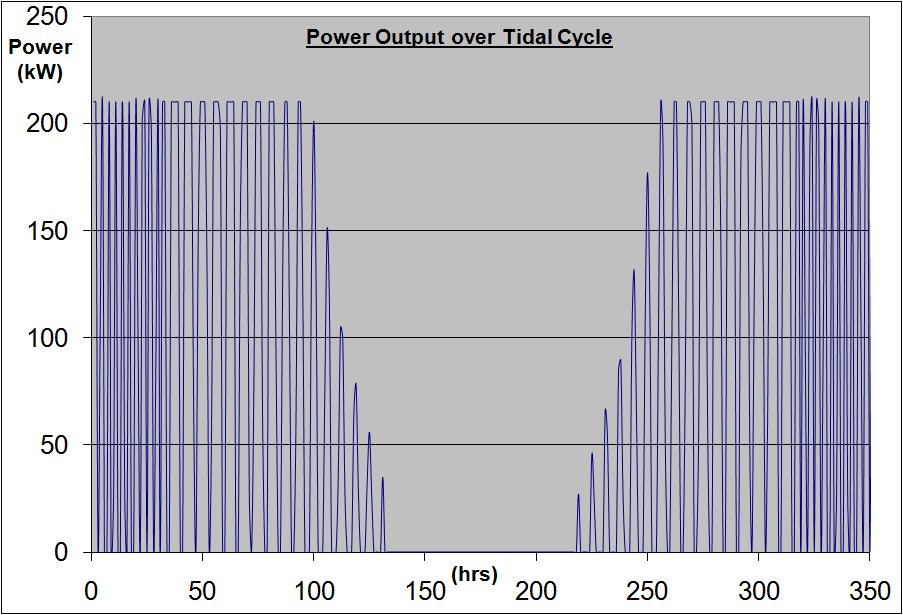
The tidal model allows us to determine the variation in the power output over the tidal cycle for any rotor configuration that we wish to analyse. In order to do this, it is first necessary to obtain, for each design, a polynomial of the variation in the power coefficient over the range of velocities experienced during the tidal cycle. This can be acquired from the results obtained using the blade element momentum theory code, which is explained in detail in the technical section of this website. The output from these results can be graphed using excel and a polynomial can be easily extracted.
The polynomial can then be applied to the tidal model to allow the calculation of the power output extracted from each tidal velocity during the tidal cycle. An example of the variation in power output over the tidal cycle is displayed in the above image. Power output is calculated using the following approximation:
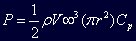
Cut in and cut out speeds of V = 1.5 and 4.5 m/s are applied to the model in order to neglect any power produced out with this range within our results. Power generated below 1.5 m/s is seen by this group to be unsuitable for large scale electricity generation and, the device is not expected to operate above 4.5 m/s due to the exceptionally high forces experienced at these speeds. Power produced by each design is also restricted to a rated power of 210 kW within the model.





