Electrical appliances
Evaluation through the excel tool
- Fridge and freezer:
We input the yearly consumption. The monthly demand is evaluated in the 'Appliances' sheet.
The consumption is averaged based on this consumption.
- Washing machine and dishwasher:
We input the yearly consumption and the number of cycles per year.
- PC and entertainment:
We input the estimated average load when running and the number of hours per day. The consumption is averaged based on this consumption.
- Lights:
We input the estimated average load when running.
We also input a seasonal percentage (estimated) of usage, typically 100% in winter months and lower percentages in other months.
The hours running are programmed directly in the hourly spreadsheet.
The resulting load is the product of the three numbers.
- Cooking:
We input the estimated average load when running.
We also input a seasonal percentage (estimated) of usage, typically 100% in winter months and lower percentages in other months.
The hours running are programmed directly in the hourly spreadsheet.
The resulting load is the product of the three numbers.
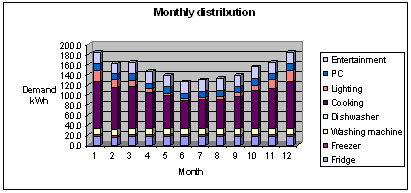
The monthly results are presented in the following graph. The data is linked to other spreadsheets automatically.
The summer consumption is lower due to lower use of lights and cooking.
Note that the March consumption is slightly higher than February due to the difference in number of days between these two months.
The total electrical appliances demand is 1827.9 kWh (or 15kWh/m2)
Domestic Hot Water (DHW)
System based on a storage tank which can store hot water produced by hybrid heat system for over a day. The heat consumption is based on daily water consumption. We input the number of people living in the dwelling and the average consumption of hot water per person in litres/day.
The daily consumption is estimated based upon the type of dwelling and living standards of the occupants. The estimated water consumption should also depend upon the storage temperature; most published estimations and surveys correspond to hot water at about 60°C so if the storage temperature is lower the consumption can be expected to be higher because it is used directly rather than mixing with cold water. We also input the storage temperature in the tank and the temperature of mains cold water.
The spreadsheet calculates the annual heat input requirement to heat the mains water to the storage temperature.
The data is linked to other spreadsheets and heat load is averaged out. Due to the daily storage tank, water consumption and heating exact time during the day is not critical. Our assumptions are:
- Storage T = 45C
- Daily individual consumption = 60 litres(This number takes into account the lower tank temperature)
- Mains water T = 10°C (Glasgow) or T = 15°C (Palermo)
The resulting annual DHW heat demand is therefore:
- Glasgow = 3560 kWh
- Palermo = 3051 kWh
| 