Open-source building performance simulator
A research-oriented tool for integrated energy simulation
ESP-r is a comprehensive, state-of-the-art integrated building performance simulation suite. It comprises several applications encapsulating decades of developments and provides tools suitable for models of different levels of complexity.
In undertaking its assessments, the system is equipped to model heat, air, moisture light and electrical power flow at user specified spatial and temporal resolution.
Validation
ESP-r has been extensively validated.
Validation models are available to any user through ESP-r interface.
Features
ESP-r is research-oriented, so the usability of features list below may show wide variations. Some features are accessible to beginner users' while many others require expert knowledge on ESP-r input files and/or source-code.
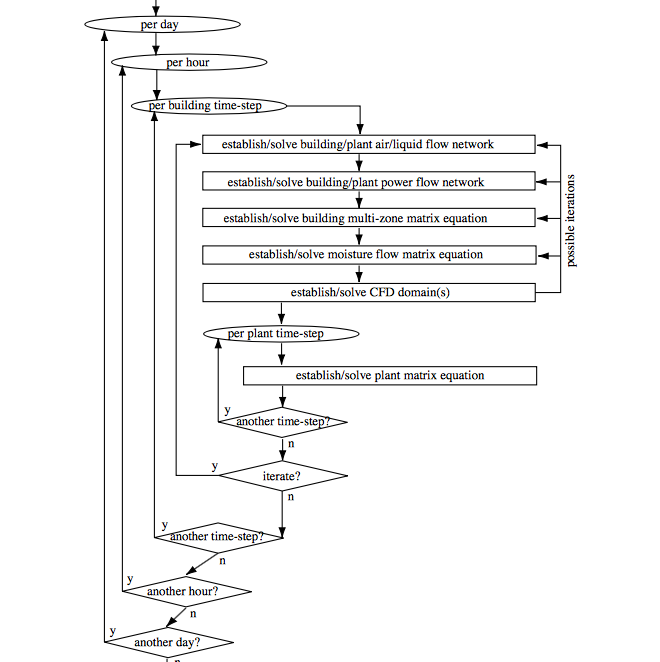
Dynamic multi-domain
Thermal zonal model, air flow, water flow, electrical flow, HVAC, CFD, and many others fully coupled calculation domains.
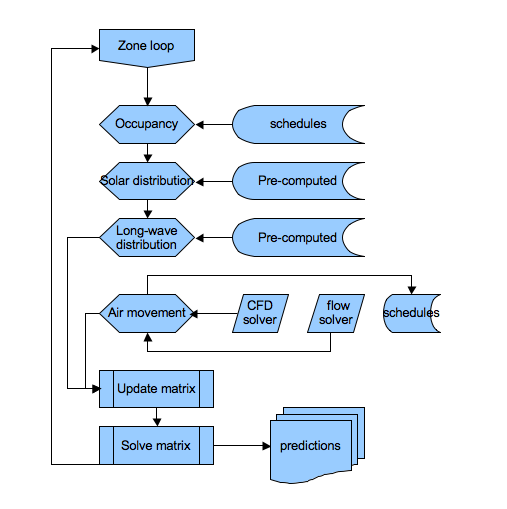
Systemic analysis
Calculations from one domain are interlinked with others, allowing assessment of unexpected interactions between different parts of the system.

Stochastic input
Capabilities to handle non-deterministic input for user-behaviour and casual gains. Coupling with obFMU, for occupant behaviour.

Time-dependant
material properties
Finite difference method capable of handling variation in properties on time-step basis, such as changes in thermal conductivity as a function of moisture content.
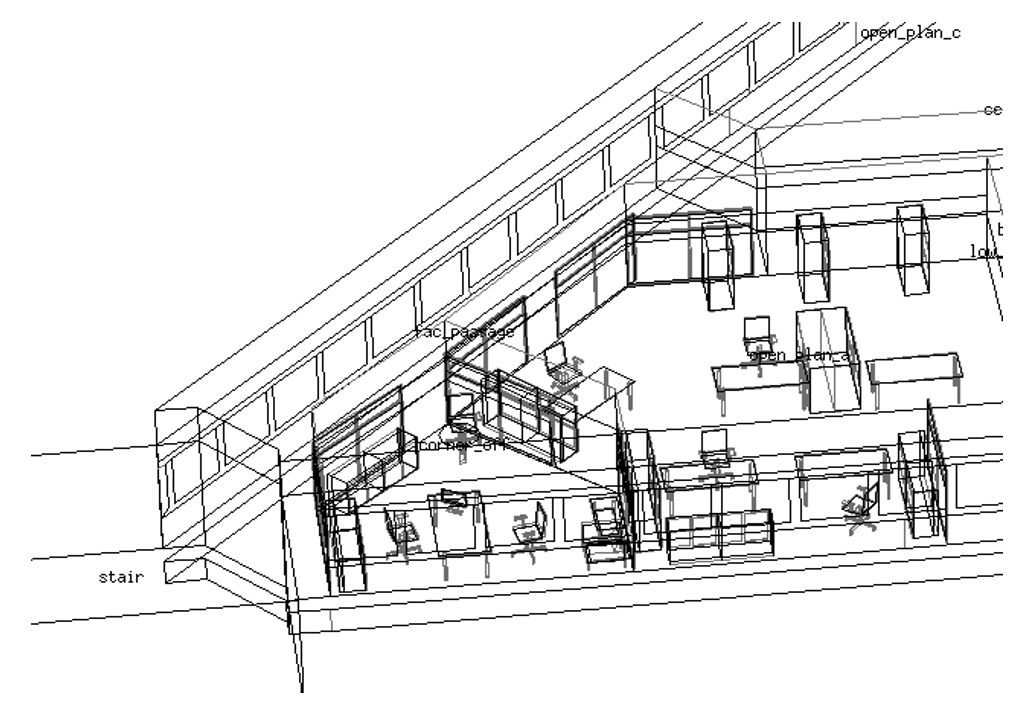
Arbitrary geometry
Capability to handle complex, non-conventional shapes.
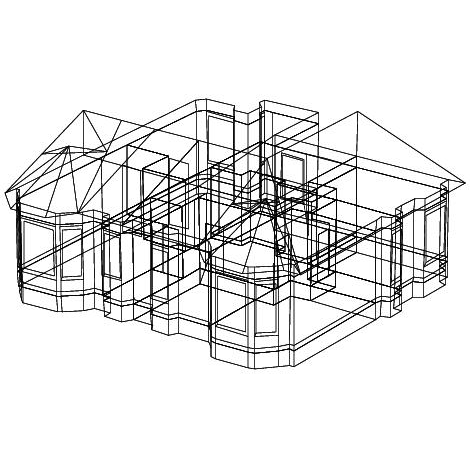
Import CAD and BIM
Cabilities to import DXF and gbXML models.

Draw zones over
scanned floorplans
Complex buildings can be easily modelled based on existing drawing.
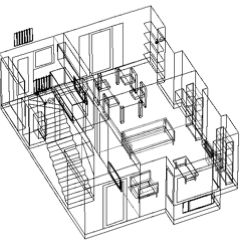
Explicit thermal mass
Furniture can be modelled considering its materials and geometry. Effects accounted for thermal inertial, moisture buffer, shading, longwave radiation, and convection.
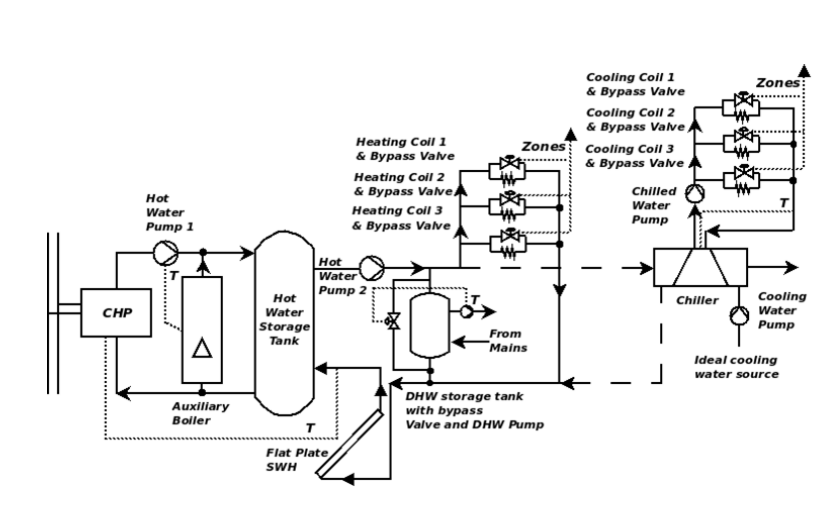
Plant module
HVAC modelling using a simultaneous solver, avoiding problems of poor convergence in complex systems.
Coupled thermal and pressure calculation in plants
Performance of pumps and fans calculated in combination with thermal effects of fluid flow.
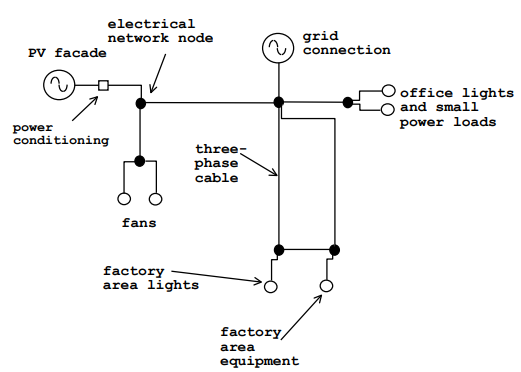
Electrical module
Detailed calculation of power flows based on equipment power factor, cables length and impedance, efficiency of inverters, etc.
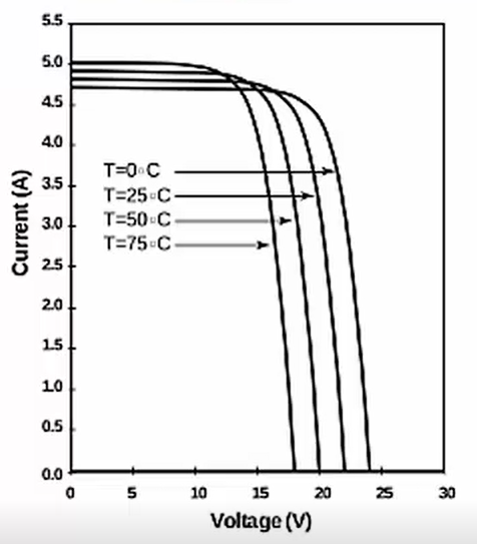
Electrical-thermal coupling
Detailed calculation of electrical performance of PV panels in relation to their temperature.
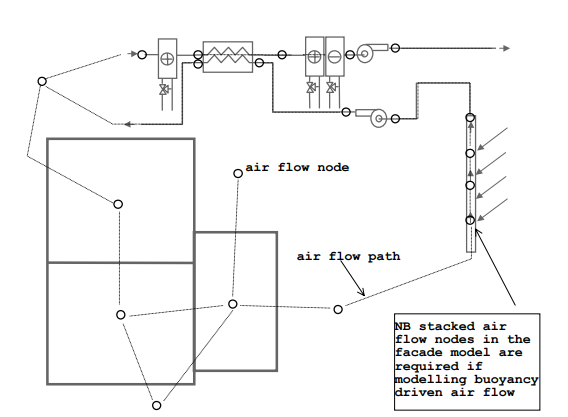
Fluid flow module
Flow networks coupled with the other ESP-r modules.
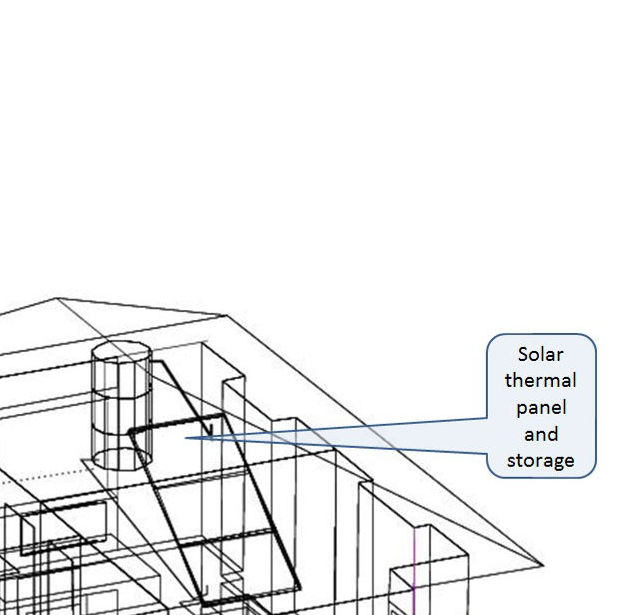
Air or water filled zones
Multiple fluid flow networks can be used to model wet systems and air movement.
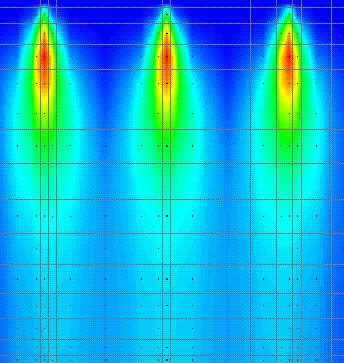
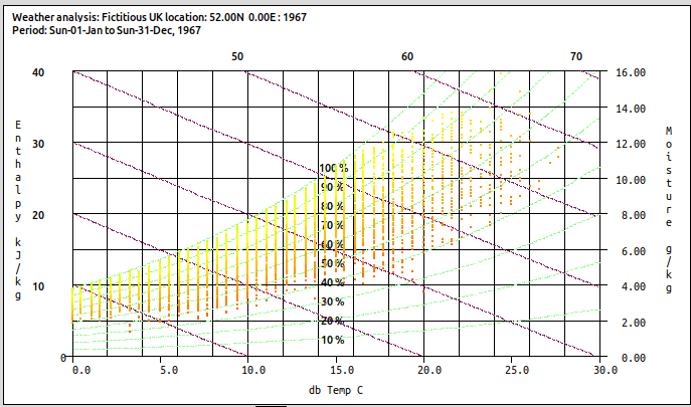
Air quality
Streamlined workflow with Paraview to facilitating visualization of CFD. Detailed assessment of CO2 concentration
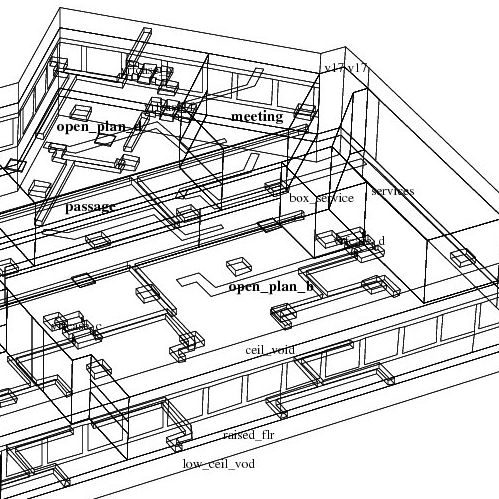
HVAC components as zones
Capability to explicitly model ducts, AHU and other fluid flow components as thermal zones.
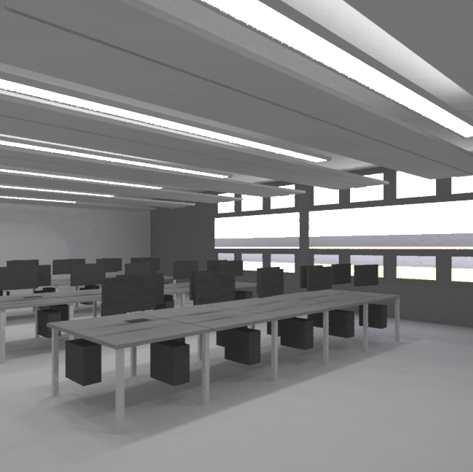

Lighting simulation
Radiance simulations integrated in ESP-r. Results can be linked to internal gains due to natural and artificial lighting.

Glare risk
Automated calculation using Radiance, with results post processed using EN-ISO standards.

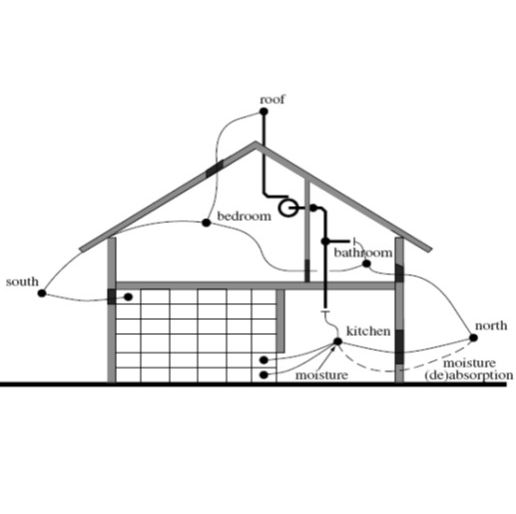
Moisture transfer module
Vapour transfer to porous materials, coupled with airflow network and HVAC performance.
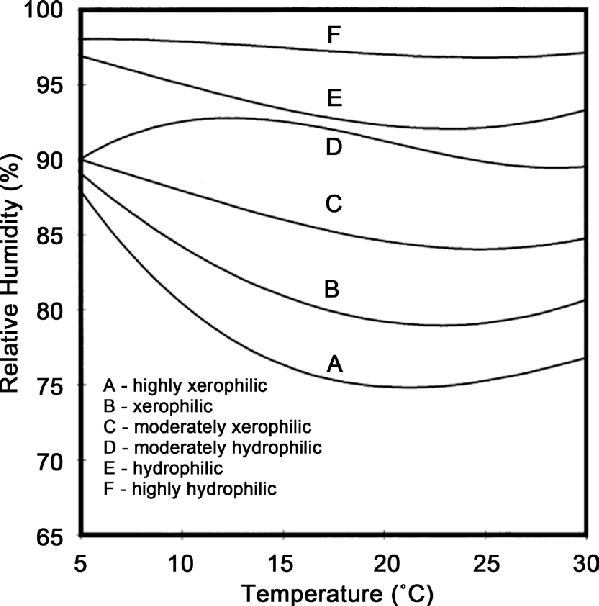
Mould growth risk
Results of temperature and moisture contents post processed to indicate mould growth risk per surface.
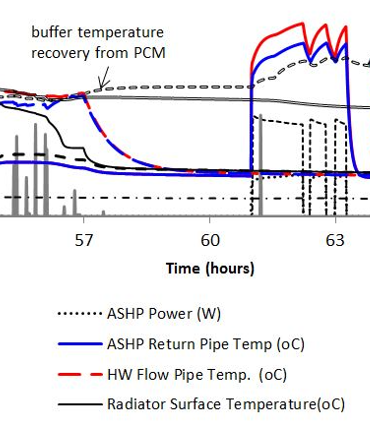
Phase change materials
PCM models available, as well as other dynamic material properties.
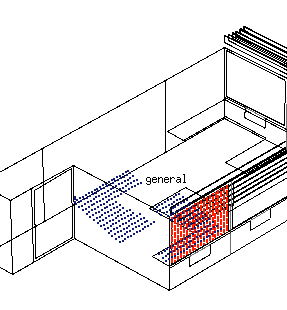
Detailed solar calculations
Solar radiation gains per surface in the indoor environment using raytracing.

Multiple convection
empirical models
Dozens of empirical equations implemented covering many convection regimes.
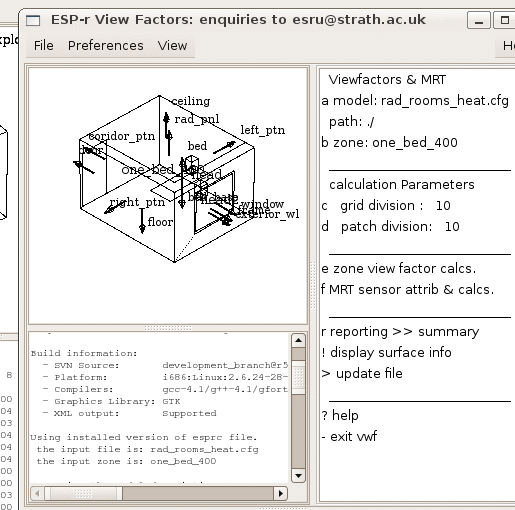
View factor calculations
Longwave radiation exchange based on calculated view factor between surfaces, instead of area-weighted factors.
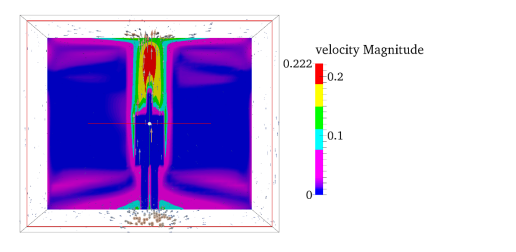
Local thermal discomfort
PMV, radiant asymmetry, thermal stratification, floor/ceiling gradient, and draught risk can be assessed covering all indicators described on ISO-7730.

Temporal files
Time-series can be imposed in any node providing greater control over the model to simulate unusual systems or for validation purposes.
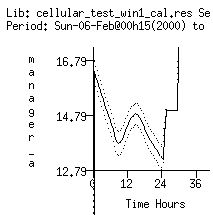
Automatic calibration
Integration with Calibro for automatic model calibration against experimental data.
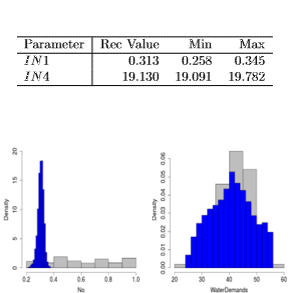
Sensitivity/Uncertainty analysis
Integrated routines for Factorial analysis or Monte Carlo simulations.
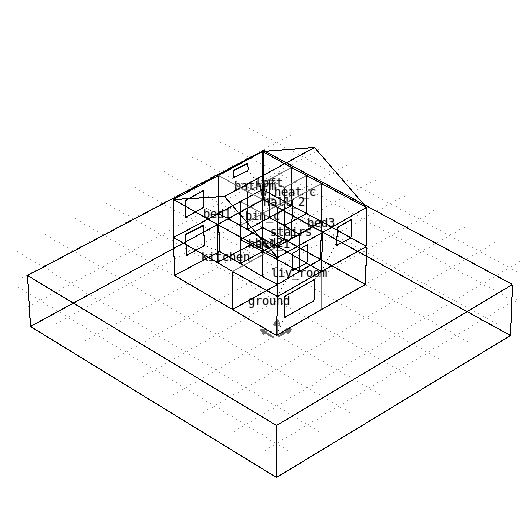
3D ground modelling
Heat flux from/to buildings calculated based on 3D ground model.
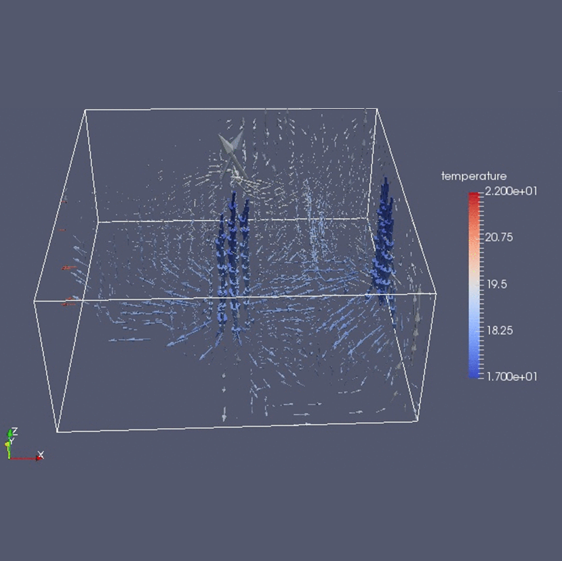
CFD for every time-step
Fully coupled CFD solver interacting with the thermal domain.
CFD-AFN coupling
Capability to model parts of the building using CFD and use air flow network results as boundary conditions.

Complex fenestration
Window properties can be changed on time-step basis to emulate controls and/or dynamic properties.
Fast simulations
The code is written in Fortran, prioritizing simulation speed. Calculation engines are optimized to reduce computation time.

Fully scriptable
ESP-r can be run in text mode and has a straightforward scripting language that facilitates automating repetitive tasks.
Single source code for calculations and GUI
The same executables handle user interface and calculations, facilitating the development of the GUI by researchers.
X interface
ESP-r uses a low level library for its interface, so developers can implement any required feature facing minimal constrains.

Modularity
ESP-r is a suite of 20 applications, ranging from pre-processing tools, calculation engines, visualization, and post-processing tools.

Research-oriented
ESP-r is done for researchers and to researchers. Advances first seen in ESP-r were often ported to commercial software.

Knowledge repository
ESP-r source code has millions of lines and documents many of the advances in the field in the last decades.

Portability
ESP-r was compiled in a variety of Unix and Linux distributions and computational infra-structures, from Solaris workstations to Raspberry Pi.
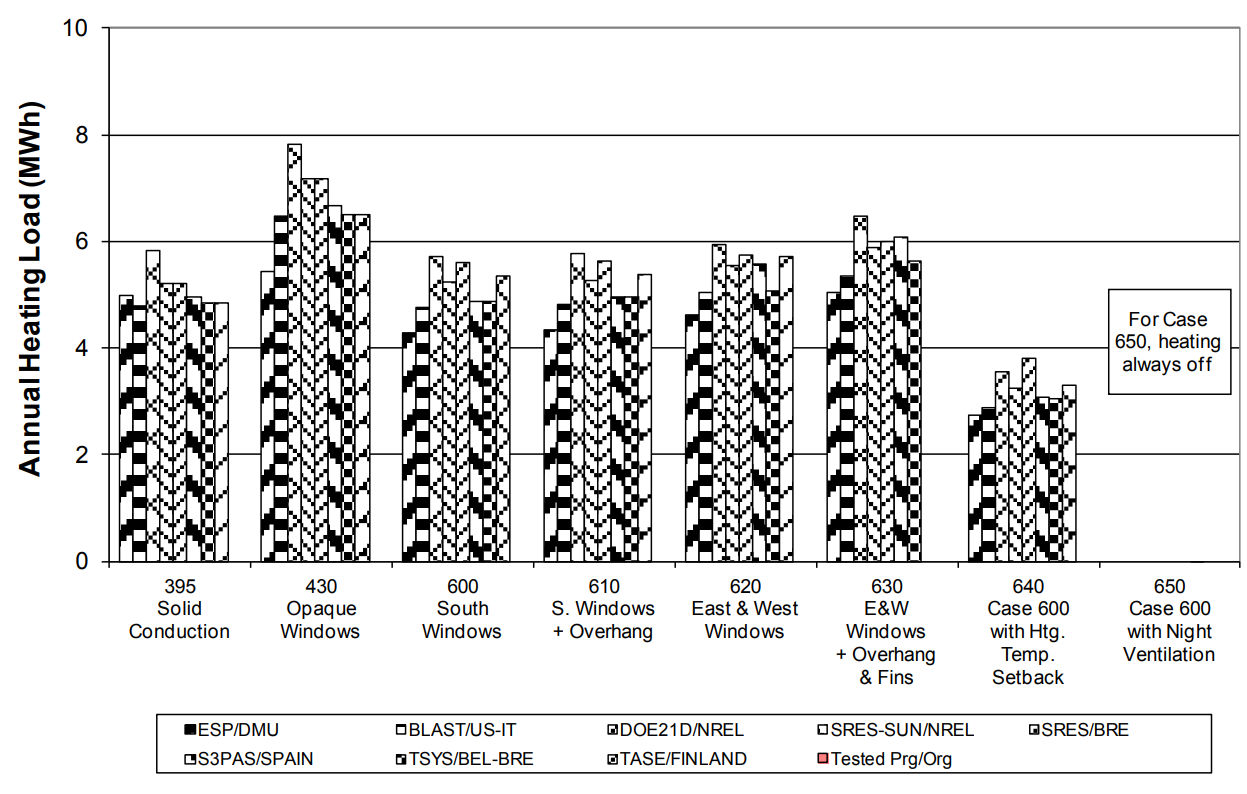
Tester
ESP-r releases are compared to results of previous models to assure calculations are as reliable in new versions as in previous ones.

QA report
ESP-r provides comprehensive reporting tools to document the model for quality assurance and/or convey information to other stakeholders.
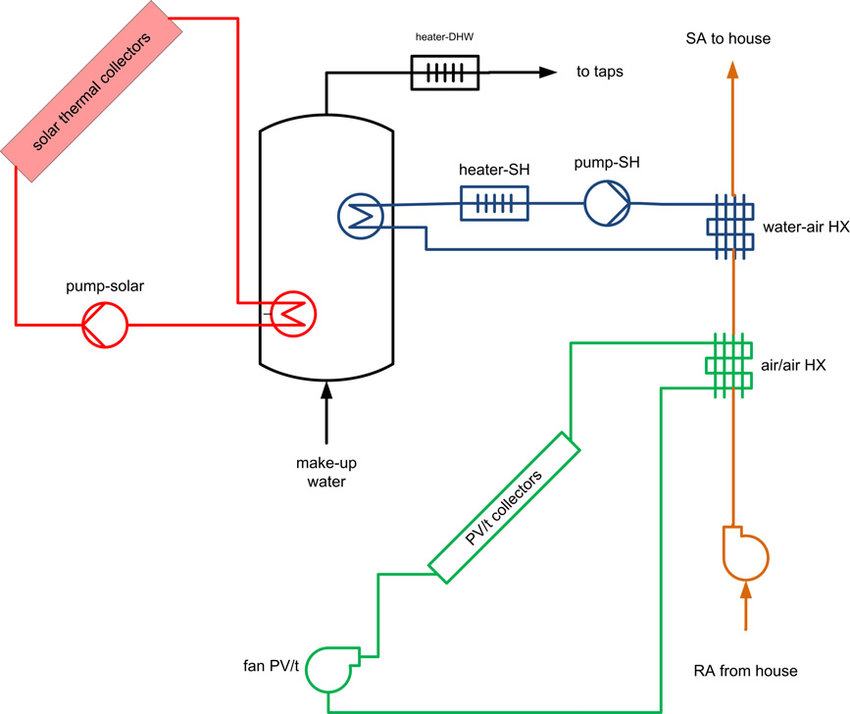
Coupling to TRNSYS
ESP-r can exchange information during runtime with TRNSYS to model complex HVAC systems (http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2012.11.060).
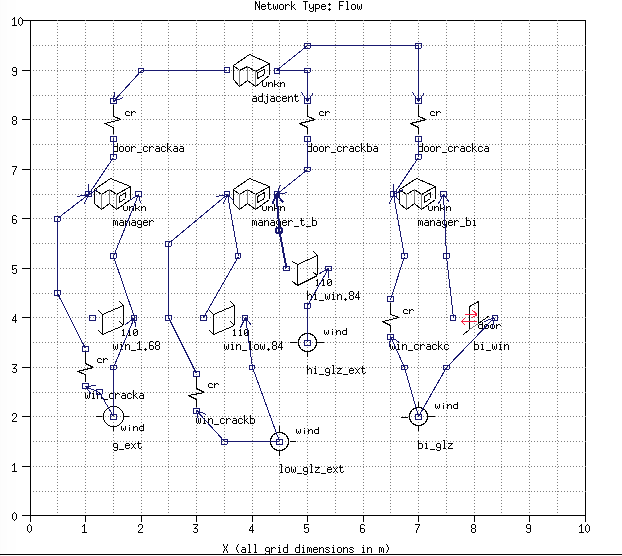
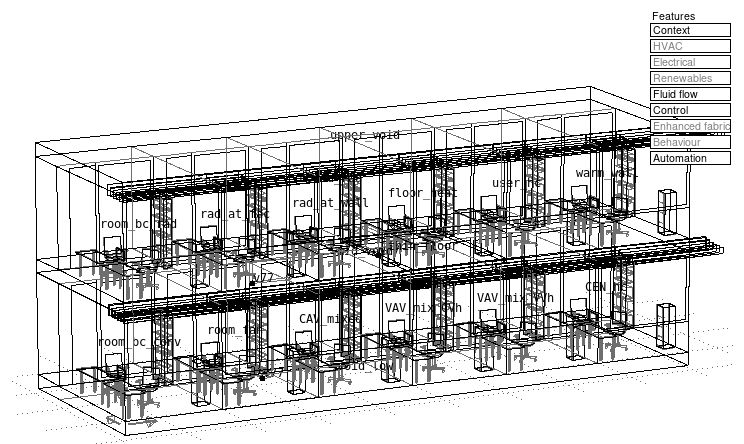
HVAC graphic representation
Graphic network topology creation tool which it typically used to create air flow networks
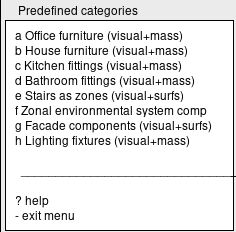
Pre-defined entities
ESP-r has a library of components and furniture for the high resolution modelling.
