| Hybrid Energy Systems in Future Low Carbon Buildings |  |
| Introduction | The team | Support | Site map |
|
|
The following table demonstrates several identical numbers concerning the different technologies and the graph below shows us what the achieved efficiencies in the lab relative to the various PV are.
|
| There will be clearly 2 types of products for some upcoming time and the space availability would be the deciding factor for each case: ♦ The expensive ones but with high efficiency per m2 ♦ The cheap ones with lower efficiency per m2 | |
The solar cells industry has expanded dramatically during recent years due to the growing demand for applications and usage of renewable energy systems. The target of the PV's industry is to decrease their cost while improving their efficiency at the same time. Their cost is relatively high today but prices are continuously falling as time goes on and the additional initial cost is even lower taking into account that we don't spend the money needed to use conventional construction materials. |
|
| The lowest retail prices (excluding sale taxes) for the different PV technologies are:
♦ Monocrystalline --> 1.68€/Wp The industry is targeting 1€/Wp for polycrystalline and thin film PVs. [7] The following table presents the prices for different PV modules.
The PVs and their mechanisms require low maintenance (only a small part of their cost) and they have typically a duration life of 25 - 30 years. PV panels can be recycled, offering the opportunity to reuse materials that have been used during the production process. Another significant aspect is that after 25 years they are able to provide over 80% of their initial power output. For instance for the PV module BP3230T, the BP solar provides the following warranty : [8] The module price stands for about 50% to 60% of the total installation cost for BIPVs, since money is also spent on wiring, meter, inverter and their placement - installation. Therefore, the bigger our integrated PV system, the lower its price/kWp. The indicative cost for the whole installation of a PV system of 1kWp is about 6,000 to 7,000 £/kWp and for a 5kWp one about 5,000£/kWp. When the PV system is integrated the cost is 8,000 to 9,000 £/kWp [9].An indicative household consumes around 3,000 - 4,000 kWh/year and a 1kWp to 5kWp PV installation can cover between 25% and 100% of its requirements depending on its location across Europe and the total installed power output. [10]
Many governments provide motives (feed-in tariffs) in order to increase the amount of the installed PVs and therefore decrease their CO2 emissions. Some indicative feed-in tariffs for 3 European countries are: The yearly sum of global irradiation [kWh/m2] on PV panels which are south oriented and optimally inclined in European countries, for an average during the period from 1981 to 1990, is illustrated on the following map. The amount of electricity which is generated by 1kWp PV system [kWh/kWp] is, for a system that has a 0.75 performance ratio. Furthermore, on the top right of the map, you may notice the optimum angle for placing the PV panels across the whole Europe in order to achieve the maximum energy output during operation. |
From the above map, we can roughly divide the European countries into 4 zones. |
Zone 1: < 750 kWh/kWp
|
Zone 3: 1000-1250 kWh/kWp
|
| As already mentioned, the orientation and the tilt angle of the PV panels affect their performance significantly. If they are optimally inclined we can achieve a 9-26% increase upon their electrical output compared to the electricity which is produced by a horizontally placed PV. Thus, we acquire an output of 760kWh/kWp in Scotland and 1510kWh/kWp in Portugal. The highest influence is noted in the Northern countries (Scandinavia) and the lowest in Southern Greece. |
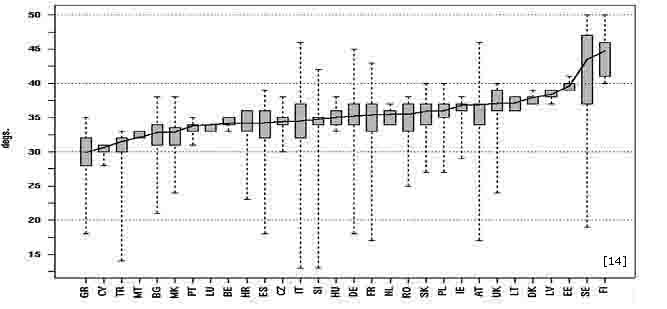
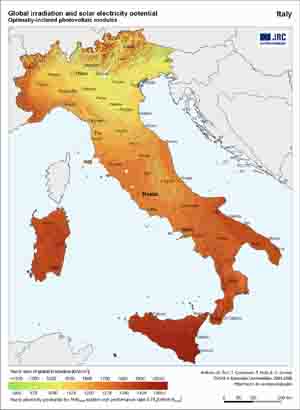
Optimum inclination angle for a South-facing PV module Since our 2 case studies are in Glasgow and Palermo respectively we provide more specific maps concerning global irradiation and the relevant produced electricity by the PVs for the United Kingdom and Italy. |
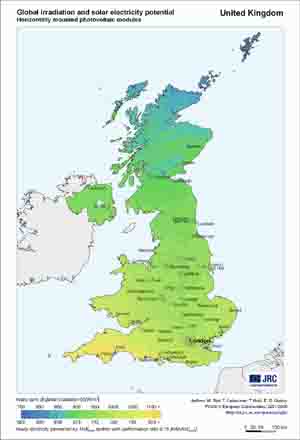 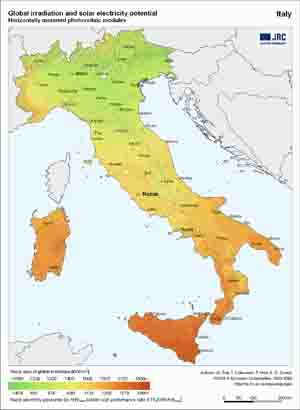 |
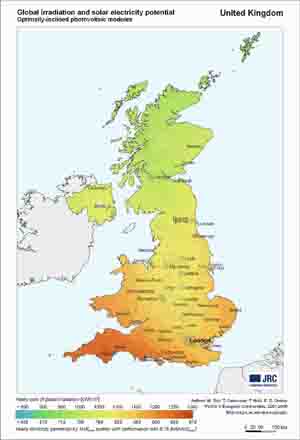  |
| Available performance calculator for grid- connected PV Systems References [1] Small "Hybrid" Solar and Wind Electric Systems Images source: Click on the images to see the source |