Nitrogen
Oxide and Nitrogen Dioxide, commonly referred to as NOx, are widely
regarded to cause health problems and Environmental Impact upon release
into the. NO is more readily emmitted to the atmosphere as a primary
pollutant, from traffic and power stations, and is often oxidised
to the more toxic nitrogen dioxide following dispersal. Road Vehicles
are responsible for over 50% of the emissions of nitrogen oxides in
the UK. Annual mean concentrations of NO2 in urban areas are generally
in the range 10-45ppb. Levels vary significantly throughout the day,
with peaks generally occurring twice daily as a consequence of "rush
hour" traffic.
Formation
of NOx
Three reaction paths, each with unique characteristics,
are responsible for the formation of NOx: Thermal NOx is formed during
high temperature processes that result in the combination of atmospheric
Nitrogen and Oxygen
Fuel NOx is formed througfh the oxidation of fuel-bound
Nitrogen in motor vehicles, electric utilities, and other industrial,
commercial, and residential sources that burn fuels.
Prompt NOx is formed by the reaction of fuel derived
hydrocarbon fragments with atmospheric Nitrogen.
It is also worth noting that denitrificating bacteria
form Oxides of Nitrogen as part of the natural nitrogen cycle.
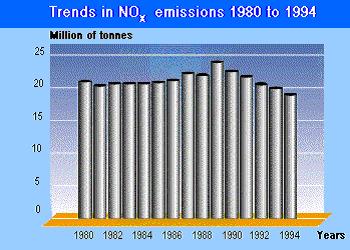
-
SOURCE – World Health Organisation and European environmental
agency.
Health
and Environmental Problems Associated with NOx
Ground level Ozone or smog is formed when NOx and volatile
organic compounds react in the presence of heat and sunlight. Children,
asthmatics, and people who work or exercise outside are susceptible
to adverse effects such as damage to lung tissue and reduction in
lung function. The pollutant is also suspected to have carcenogenic
and mutagenic properties. In addition visibility in cities can be
impared, and a unsightly red-brown haze may be observed at dusk.
NOx and sulphur dioxide can react with other substances
in the air to form acid rain which can cause deterioration of cars,
buildings and historical monuments; and cause lakes and streams to
become acidic and unsuitable for numerous species of aquatic life.
NOx reacts with ammonia, moisture, and other compounds
to form nitric acid and related particles. Human health concerns include
effects on breathing and the respiratory system, and damage to lung
tissue. Small particles penetrate deeply into sensitive parts of the
lungs and can cause chronic respiratory disease such as emphysema
and bronchitis, also aggravate existing heart disease.
Water Quality Deterioration can be caused by increased
nitrogen loading in receving waters, particularly coastal estuaries.
Additional nitrogen may contain a considerable BOD load, causing nitroficating
microorganisms to thrive, accelerateing "eutrophication," and “agal
bloom” which leads to oxygen depletion and reduces fish populations.
Nitrous oxide is a greenhouse gas, which accumulates
in the upper atmosphere. Some scientists believe the pollutant contributes
to the “Greenhouse Effect”