|
Back to home page Transmission of Renewable EnergyIntroduction to our project
Studying
the current scheme of transmission and distribution networks we
can notice the increasing levels of
distributed generation(embedded generation).This is occur
because of the ongoing usage of distributed generation with CHP
and renewable sources and
also the advantages that distributed generation offers. In
our project we tried to study the transmission of renewable energy
in co-ordination with distributed generation and we focused in a case study in order to derive useful conclusions about the economical,environmental
and social feasibility of using distributed generation for the transmission of renewable energy. Distributed generation can be defined as power generation that is connected directly to the distribution network instead of the transmission electricity grid
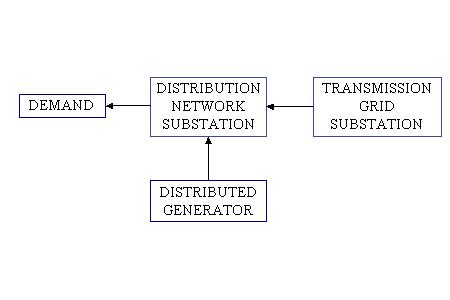
This is a typical figure for distributed generation
,where we can see the connection of the generator not to the transmission
grid but directly to the distribution substation
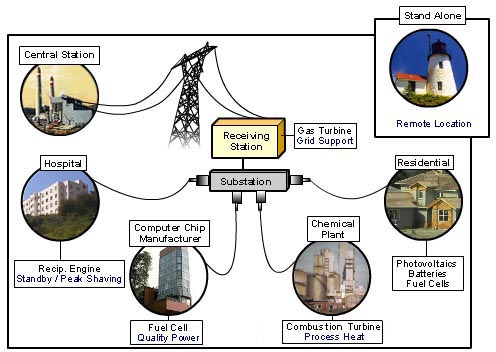
Distributed generation can be used for various
purposes and by that we mean
Currently
in Scotland there is installed capacity from distributed generation
about 1771 (one thousand seven hundred and seventy one MW) and is expected to reach 2250-2500
MW by the year 2005. In
this Pie Chart we have the percentage for both centrally dispatched
and distributed generation in Scotland. 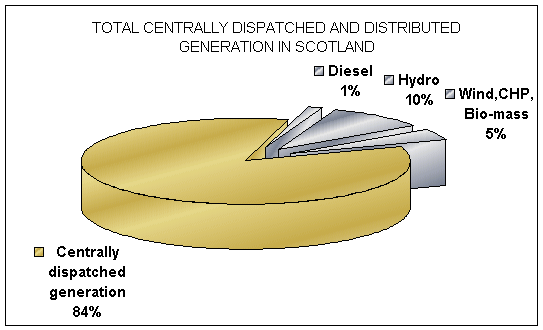
Although
the continuant increase of D.Generation, there are certain barriers
that have to be examined very carefully in order to succeed further
development of DG in the future. There
are some are
not technical and have to do with: -the
regulatory
framework(for example deep charges should not be paid solely
by new distributed generators as they are not the only
party responsible for the connection
reinforcements ,but the changes should divided amongst all contributing
generators) -grid
connection issues -planning permission and
the technical barriers
have to do with -forecasting
and scheduling of Demand and supply
in connection with location and time of the year -and also various problems that have to do with controlling and measuring D.G Back to home page |