Every Unit (kWh) of electricity
produced by renewables can displace a unit of electricity, which would
otherwise have been produced by a power station burning fossil fuel. Most
renewable electricity cannot replace electricity from nuclear power stations
because these operate at 'base load', that means they are working for
the whole time that they will be available. Taking into account the hypothetical
savings that have been illustrated in the previous examples we can begin
to get a picture of how these changes in behaviour could help Scotland
meet environmental targets that have been set for 2010.
The purposes of the examples are to demonstrate how we could go about
reducing CO2 emissions in our everyday lives, whilst also saving money.
It also highlighted the national impact that these changes could have.
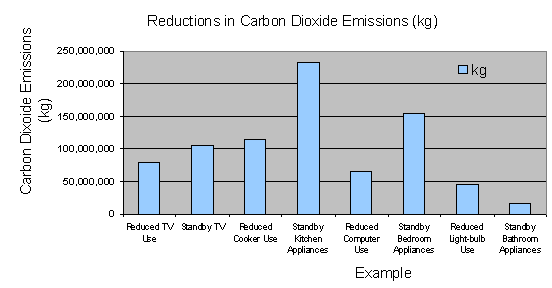
1. Living Room
i) Annual reduction in emissions due to switching lights off during breakfast
(1 hour a day) and watching one hour less TV a day.
0.97kg x 81,057,375 kWh/year = 78,625,653 kg/CO2
ii) Annual CO2 emissions due to leaving TV and Video on Standby;
0.97kg x 108,383,175 kWh/year = 105,131,679 kg/CO2
Emissions = 183,757,332
kg/CO2
4.6 % of Household CO2 Emissions (4.6% of 3,983,250,000 kg)
0.25 % of Total CO2 Emissions (Scottish total = 72,300,000,000 kg)
2. Kitchen
i) Annual reduction in emissions due to using microwave for 45 minutes
instead of cooker ring for 2 ½ hours a week
0.97kg x 118,609,200 kWh/year = 115,050,924 kg/CO2
ii) Annual CO2 emissions due to leaving selection of kitchen appliances
on Standby;
0.97kg x 239,449,725 kWh/year = 232,266,233 kg/CO2
Emissions = 347,317,157
kg/CO2
8.7 % of Household CO2 Emissions (8.7% of 3,983,250,000 kg)
0.48 % of Total CO2 Emissions (Scottish total = 72,300,000,000 kg)
3. Bedroom
i) Annual reduction in emissions due using home computers for one hour
less per year
0.97kg x 66,689,122 kWh/year = 64,688,448 kg/CO2
ii) Annual CO2 emissions due to bedroom appliances left on Standby.
0.97kg x 159,344,100 kWh/year = 154,563,777 kg/CO2
Emissions = 219,252,225
kg/CO2
5.5 % of Household CO2 Emissions (5.5% of 3,983,250,000 kg)
0.3 % of Total CO2 Emissions (Scottish total = 72,300,000,000 kg)
4. About the house
i) Leaving hall lights off in the morning. Assume two hall lights
(saves 7 hours electricity per week
0.97kg x 46,318,500 kWh/year = 44,928,945 kg/CO2
ii) Annual CO2 emissions due to bathroom appliances left on Standby.
0.97kg x 16,676,775 kWh/year = 16,176,471 kg/CO2
Emissions = 61,105,416 kg/CO2
1.5 % of Household CO2 Emissions (1.5% of 3,983,250,000 kg)
0.08 % of Total CO2 Emissions (Scottish total = 72,300,000,000 kg)
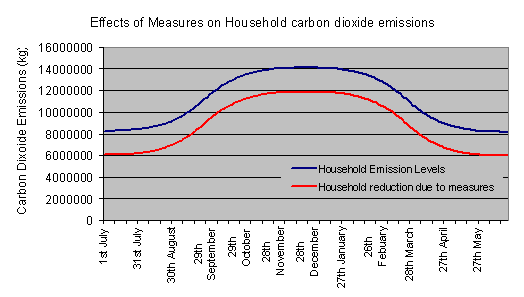
Conclusions
For the purpose of our demonstration we have shown eight relatively examples that could help reduce CO2 emissions from the effects of household electricity. These savings could prevent the annual emissions of 811,432,130 kg/CO2
20% of household electricity
CO2 emissions in Scotland could be potentially saved from the Scottish
total household emissions of 3,983,250,000 kg/CO2.
Remember that electricity carbon dioxide emission were only responsible
for 6% of Scotland's emission total. The purpose of this example is not
to show that we can reduce total Scottish carbon dioxide emissions by
20% just by switching off a few lights and plugs.
However if the same type of logic was applied across the board, we could go a long way to meeting environmental targets that currently seem unachievable. If we can reduce the amount of electricity we use then perhaps there is a greater chance of renewables making a greater impact and providing greater security of supply.
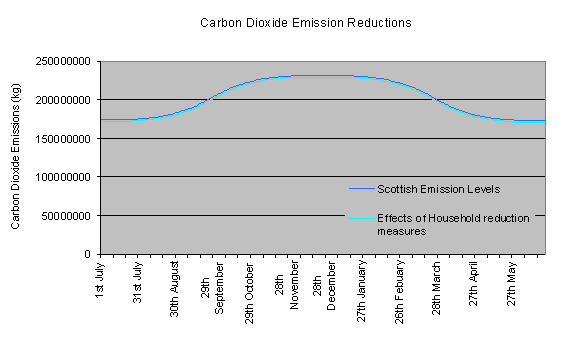
Our measures only result in a 1% reduction in the Scottish total
![]()
Home, Urban, Standby, Cutting the cost, Consumption guide
![]()