 |
The
purpose of this experiment was to operate the fuel cell under different pressure
conditions so that the effect of pressure on the reaction rate could be
investigated. This is only achievable by placing the fuel cell in a glass
chamber, which is evacuated by a vacuum pump, reducing the pressure below the
atmospheric one.
The
equipment used for this experiment is illustrated right below:

A
glass chamber, a thermometer with a thermocouple device, a multimeter, a pump, a
gauge pressure and sealing materials attached to cables are all part of the
equipment.
The
same experiment took place twice. Once with four – mole concentration solution
and another one with two – mole concentration so that a clearer view of the
effect of pressure on the fuel cell operation could be established.
The
results from the measurements are summarized on the following table:
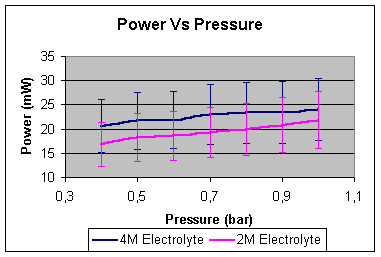
From
graph it can be noted that by reducing the pressure of the fuel cell
surroundings the reaction rate it is also being reduced.
The
experiment was done with pressures below the atmospheric due to equipment
limitations, but it is obvious that increasing the pressure above the
atmospheric one, the reaction rate would also be increased.
Hence,
as the reaction rate is reduced or increased, so and the power output is being
reduced or increased in the same manner with the reaction rate.
Apart
from that, the total cost of a fuel cell operation under this conditions it is
also affected by costing more money for such a fuel cell arrangement.