D.3 Combine
Demand Profiles
|
Exercise purpose: |
To know how to combine different demand profiles to get the total demand
profile. |
|
|
|
|
1. Make a combined
profile. |
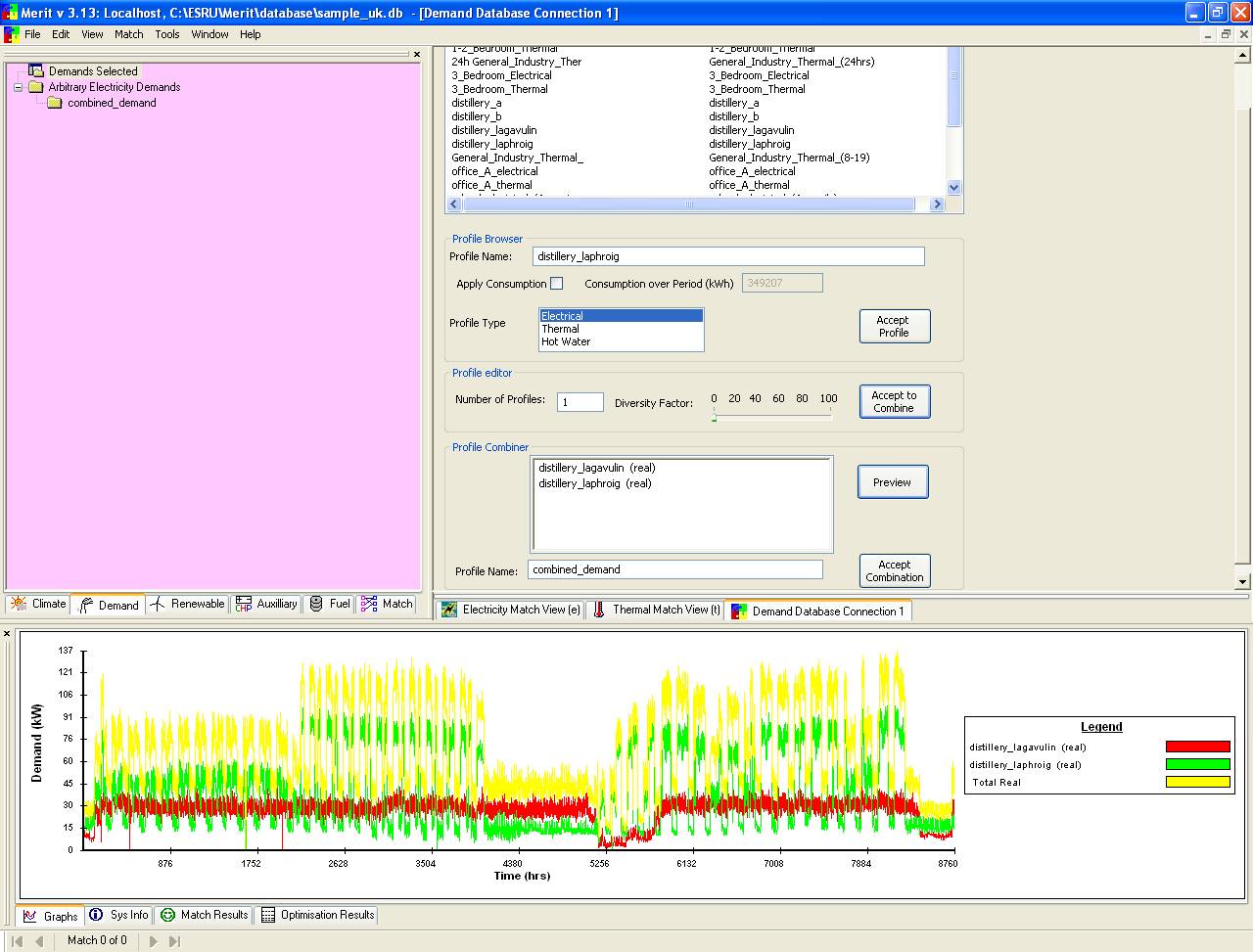
Although individual demands may suit your purposes, you can also combine one or more profiles to achieve the total demand profile at various scales. To do this, use the Accept to Combine button instead of the Accept profile button. Here is an example: Make a combined profile of the demands of two distilleries, assuming there is a plan to adopt a renewable energy system serving both distilleries. Double click on ‘distillery_laphroig’ in the list of demands and the click on the button ‘Accept to Combine’; the selected item will be shown in the box of the Profile Combiner area beneath the Profile Browser area. Select ‘distillery_lagavulin’ as the second profile to be combined and click the Accept to Combine button. You need to
give this combined profile a name. For this exercise, type ‘combined distilleries’
in the field of Profile name. Finally, click the Accept combination button. It should result in the image shown below. In the upper-left frame there is a new item called ‘combined_demands’ with two sub-items. When clicking the combined item on the tree, the graph of the combined profile will appear in the bottom window frame. NOTE: -Merit supports up to nine single or combined profiles. -To remove a profile of the ‘Demand Profile Selected’ tree in the upper-left frame, right-click on the name of the profile and then select Delete. -Merit offers a number of advanced features which will be covered in a later exercise. The Profile Combiner interface has a Number of Profiles: field which can be used to scale up the current combined profile to represent, for example, a number of buildings. There is even a Diversity Factor which can be applied to make the scaled profile more realistic.
|
|
|
|
|
Exercise result: |
Ability
to combine two demand profiles and achieve the total demand profile. |
|
This is the end of Demand Profile Session. |
|