Energy systems: Environmental Impact
Assessment
On this
page we consider sustainable project development, the
Environmental Impact Assessment process, and the
environmental
impacts of biofuel - fuel cell based energy systems.
Sustainable
project development
Progressive
approaches are required to meet growing energy needs and achieve
a shift towards sustainability. These ideas are discussed on our sustainable energy needs page.
Globally,
biofuels are likely to provide a major renewable energy
contribution, and fuel cells offer the most efficient means of
converting the limited quantities of biofuels (or fossil fuels)
to electrical energy.
Fuel
cells have other significant environmental advantages including
low emissions, and the available information does not suggest any
fundamental environmental problems.
However,
initially at least, fuel cell systems will be of higher capital
cost than established technologies. Our general approach to
Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) is to determine whether a
fuel cell system will give a sufficient return on the investment,
both in environmental and economic terms.
Integrated
project management and Environmental Impact Assessment
To
maximise the overall benefits of a project, the environmental
assessment process should be seen as an opportunity to improve
the infrastructure and technology. Thus the project should :
- Meet
human needs and those of the organisation
- Develop
effective technology (efficient, accessible, &
affordable)
- Include
systematic and inclusive Environmental Impact Assessment
- Promote
financial innovation (work with real values and costs)
Environmental
Impact Assessment process
The
scope of the assessment
Before
undertaking the assessment it is necessary to identify the
purpose (compliance, improvement, investigative) and scope (system,
installation, product, local, regional, or global) of the
assessment, and who the assessment is for (the stakeholders).
We have
designed a general assessment method which can be adapted for any
situation, but our primary objective is to determine the best
global environmental option and the influence of other factors.
| Describe the nature of the
development We are considering
projects to provide energy to meet human needs. They may
be in the developed or developing world; for urban,
rural, or remote locations; and community or process
applications.
Identify
environmental aspects and agree their significance
Our
method is designed to prioritise the significance of
environmental aspects, using an inclusive process, to
facilitate effective investment in the environment.
There
are many aspects to assess and impacts to address. The
method should ensure effort for quantitative analysis and
improvement actions are committed to the right areas.
Assess
the environmental performance
The
scheme performance is assessed and the resulting
environmental impact evaluated under each aspect using
detailed assessment methods such as resource use planning
and life cycle assessment, or risk assessment, depending
upon the purpose of the assessment.
Environmental
improvement measures
The
assessment will show the most significant adverse
environmental impacts, and attempts should be made, in
order of preference; to avoid, prevent, or mitigate these
impacts using a participative approach, technical, or
economic means.
|
| Describe the nature of
the development
Scope of
application & impacts
Alternative
scenarios
|
| Identify environmental
aspects
Agree significance
Indicators &
comparative data
|
| Assess environmental
performance
Resource use
planning
Life cycle
assessment
Risk assessment
|
| Environmental
performance improvement
Avoid adverse
impacts
Prevent adverse
impacts
Mitigate adverse
impacts
|
Environmental
Impact Assessment Process
|
Establish
the Best Environmental Option
Once the
environmental assessment has been completed and environmental
improvement measures incorporated alternative schemes should be
compared. There is an increasing requirement for the Best
Environmental Option (BEO) to be chosen:
- Environmentally
and for the local community
- Economically
and commercially considering market, financial, &
legal factors
Partnerships
between the various stakeholders offer a means of meeting
conflicting requirements and constraints.
| The "Assessment" and further
information Further information on the
requirements for Environmental Impact Assessments and
Environmental Statements are given on our Environmental
aspects and impacts review page.An
indicative Environmental Impact Assessment for biofuel -
fuel cell based energy systems, using our assessment
method, is given in full on the review page.
A
summary Environmental Statement for biofuel - fuel cell
energy systems based on this assessment is included
below.
Detailed
information on our Environmental Impact Assessment method
and the associated spreadsheet is given on our Environmental
assessment method page.
|
BIOFUEL
- FUEL CELL ENERGY SYSTEMS
Environmental summary statement
Description of Need
A large
increase is required in the effective use of renewable energy to
meet increasing world wide energy demands, reduce the high
depletion rate of valuable fossil fuel reserves, and reduce
global warming. Biofuels are a major renewable energy source and
fuel cells offer the most efficient means of generating
electricity from biofuels.
Alternatives
These
include:
- Centralised
electricity generation using nuclear power: Only
appropriate where a sufficient support infrastructure
exists; Consequence of accidents, and management of
nuclear waste are major issues
- Local
electricity generation using biofuels as the fuel source, and
combustion engines or fuel cells as the prime mover: Fuel cells offer more efficient
utilisation of biofuels, and lower emissions, but initially at a higher cost
- Hydroelectricity
and tidal: Available sites limited and adverse impacts
from flooding and water use may be significant
- Wind
power: Effective sites limited and varying power output
requires connection to a large network
- Wave:
Technical development required before it can be
considered a viable alternative except at a few specific
locations
- Solar:
Limited energy available and high cost using current
technology, dependent upon climate
- Geothermal:
Mainly a source of low grade heat energy; Limited sites
and difficulty of extraction
Environmental
Aspects and Impacts
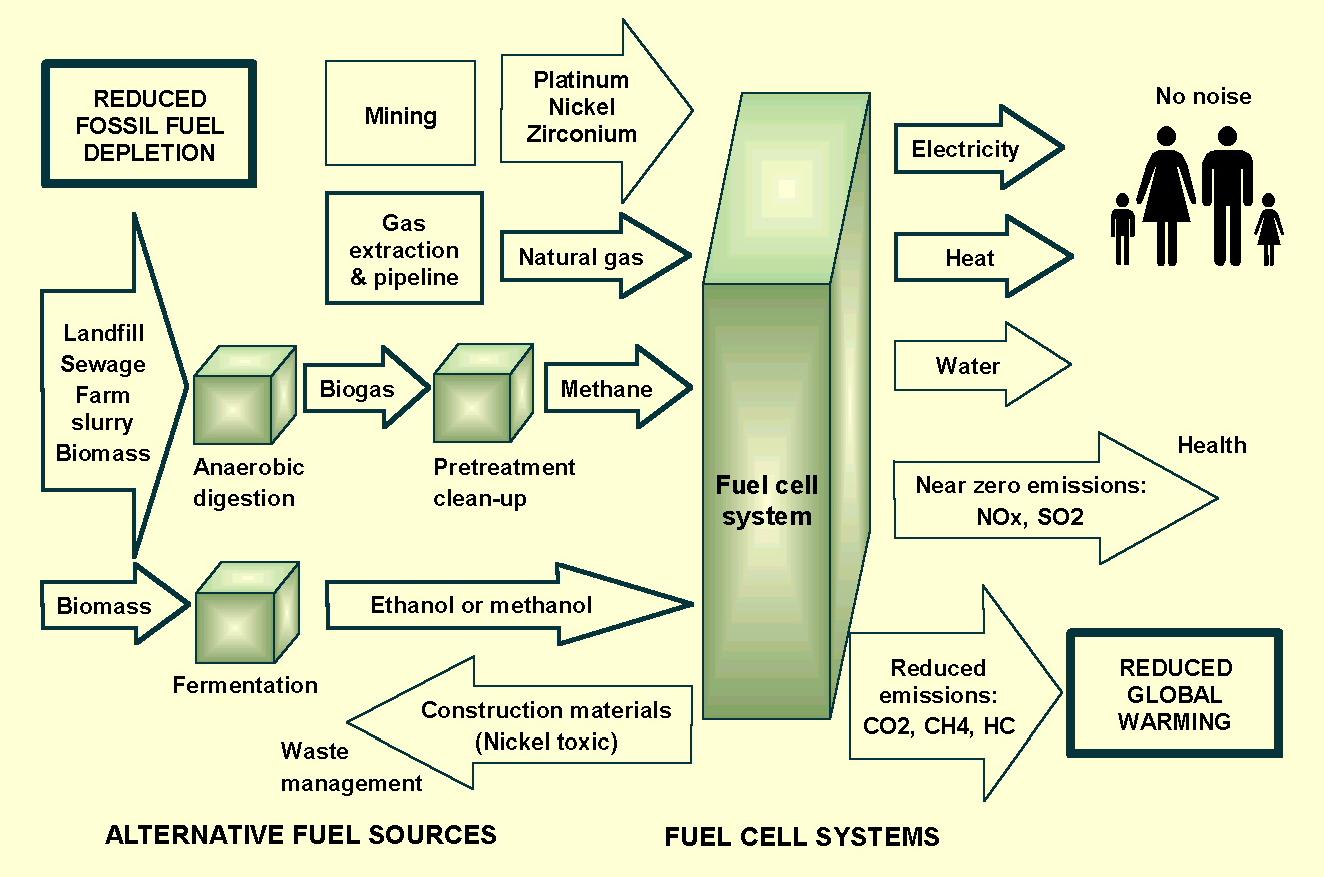 |
Environmental aspects of systems under consideration
|
Social
inclusion
Meeting growing energy demands in the developing world
A significant positive impact identified from the assessment is the
potential
to meet growing energy demands and contribute to general
infrastructure development in the developing world. However
the technology must be accessible and affordable before this
potential can be realised. Barriers to this development include
the cost of the bio-digesters, fuel clean-up equipment, and fuel
cell systems; and the lack of commercial availability and useful
information on fuel cells.
Economic
development
Risk of increased costs or loss of income
Although
the costs per unit energy may be high as described above, the
projects are small scale with low risk of increased costs or
damage to the local infrastructure causing loss of income. Low
economic risk was assigned a higher environmental significance
than return on investment using our assessment method.
|
Resource Use
Depletion of non-renewable energy sources
Electrcity is the main attribute of this era.
Coal, oil and natural gas have been fueling power generators, since the beginning of the industrial revolution.
Economic and social reasons have forced major improvements in energy systems, as far as emissions and efficiencies are concerned.
Although there has been a lot of development, fossil fuels still provide 68 % of today 's total energy supply
(Fig. 1), leading to their fast depletion.
There are two ways to overcome this issue: a. the energy conversion
schemes should have high efficiencies, and b. renewable energy schemes
must contribute a bigger part in power generation.
Reduced depletion of fossil fuels is confirmed as a major positive
environmental impact of FC systems.
|
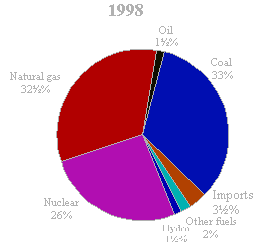 |
| Fig.1: Power generation (by fuel) - Source: DTI
|
Transport
Depletion of fuel stocks and impacts of transport fuel processing
As mentioned above, it's absolutely necessary to sustain fuel stocks. Raw fuel undergoes heavy processing and refining before it
can be used in the transport sector. Thus, thinking on a well-to-wheels basis, the product yield drops significantly.
Global Warming emissions arising from transport
Furthermore, although there have been improvements in fuels and engines and their pollutive emissions
have clearly been reduced, road transport still contributes 30 % of the total CO2 emissions, and 50 % of the
total NOx emissions.
Local health effects and disturbance arising from transport
Apart from increasing global warming and depletion of fossil fuels, excessive transport is also
associated with a lot of local problems and disturbances.
Increase in cases of asthma and other respiratory problems, is strongly related to air pollution, in urban and high traffic areas.
It's important to avoid excessive transportation and therefore, power systems that are fueled by the local or closest fuel supplies
are favourable options.
Transport impacts of FC are low compared with most of the alternative energy schemes.
|
Ecological
Impacts
Global warming emissions from use of fuels
CO2 and CH4 are the principal gases that lead
to the greenhouse effect and consequently to to global warming.
Taking into account that energy demands are likely to increase, both
in the developed and developing countries, and that power stations in the UK, in the present moment
produce ca. 35 % of the total CO2 emissions,
thorough investigation of power schemes is necessary, in order to reduce the greenhouse effect.
The main significant negative impact of fuel cells, is the emission of CO2 which
causes global warming. However, CO2 emissions are lower using
fuel cell systems than any of the combustion engine systems.
Global
warming due to methane emissions from decay of organic waste is
reduced by using the methane for energy production, where it
would otherwise be released to the atmosphere. This applies
mainly to farm slurry digester schemes reducing methane releases
from animal dung. With these schemes
there should be a net positive impact on global warming due to
the reduced methane emissions having a greater impact than the CO2
emissions from the fuel cell.
Soil erosion
Soil
erosion is reduced where digested sludge from farm slurry
digester schemes provides a good fertiliser.
Hazard to biological life cycles or ecosystems
Additionally, NOx and SOx concentrations in
the atmosphere are of great concern, not only because they can be
inhaled and cause lung cancer, but also because of the effects of
acid rain. Genetic defects and species extinction are the main
tremendous effects of acid rain on flora and fauna. Furthermore,
acid rain dissolves aluminium and other poisonous metals in the
earth and these, too, flow into lakes and rivers. The results for
aquatic life can be devastating.
There is no combustion involved in FC systems and the fuel has to be highly desuplhurised
prior to its use. Thus, FC have negligible, almost non-detectable
NOx and SOx emissions.
|
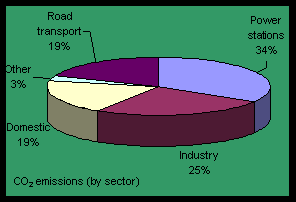
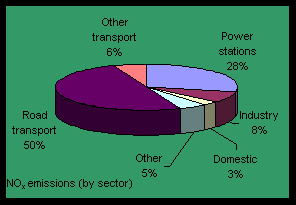 |
Fig.2: NOx and CO2 emissions (by sector) -
Source: UK NAEI
|
|
Environmental
Impacts
Air pollution and air quality
FC systems are relatively environmentally benign. Fig.3, illustrates the difference in emissions
from conventional CHP schemes and a FC CHP.
All emissions are very low except the CO2 emissions described above.
Hazard to range of natural species or biodiversity
The
biofuel - fuel cell systems have low general impact on the
natural environment, although the introduction of energy crops should be managed to avoid
spread of disease or the crops overwhelming indigenous species.
Other impacts
The
manufacturing process is manageable. Extraction and processing of
nickel is the main hazard but the quantities of nickel required
are low.
Noise
levels are low.
Pathogens may be destroyed
by higher temperature bio-digestion, and digested waste is less attractive to rodents and insects.
Hence bio-digestion can have significant health benefits.
|
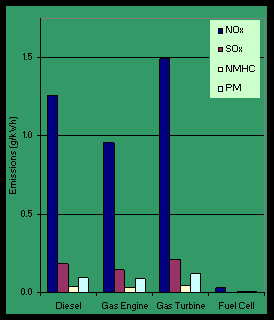 |
| Fig.3: Emissions from CHP schemes
|
Improvement
Measures
As stated
above, the main adverse environmental impact is global warming
from CO2 emissions. Improvement actions include:
- Avoid
CO2 emissions by using alternative non-combustion energy
sources to the greatest extent possible in the energy mix:
Nuclear, Hydro, Wind, Wave, Solar, Geothermal;
- Avoid
CO2 emissions by developing hydrogen fuel sources for fuel cells;
- Reduce
CO2 emissions by maximising the efficiency of the prime
movers: The order of preference is high temperature fuel
cells, low temperature fuel cells, combustion engines;
- Mitigate
global warming impact by maximising schemes which capture
methane which would otherwise be released to atmosphere.
Farm slurry digester schemes have the greatest potential.




