Biodiesel
Environmental Impacts
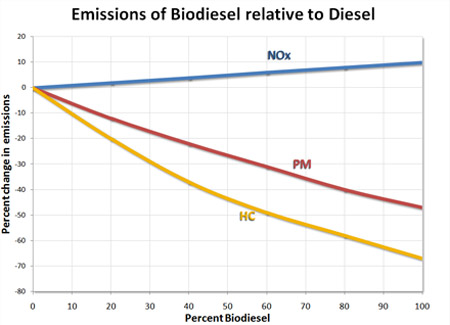 |
| Tail-pipe Emissions: Average emission impacts of biodiesel for heavy-duty highway engines (Data covers biodiesel from different feedstocks) [14] |
-
CO2 emissions: when biodiesel is burned the released CO2 into the atmosphere will be recycled by growing plants, which are later used to produce biodiesel. A study sponsored by the U.S. Department of Energy and the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDOE/USDA), concluded biodiesel reduces net carbon dioxide emissions by 78 percent compared to petroleum diesel.
-
Carbon Monoxide: the exhaust emissions of carbon monoxide from biodiesel are on average 48 percent lower than carbon monoxide emissions from diesel. Biodiesel has higher content oxygen, which helps to reach a high rate of combustion.
-
Reduced SOx emissions: biodiesel is basically sulphur-free. Therefore, oxides and sulphates from biodiesel are essentially eliminated when compared to diesel.
-
Particulate Matter: The exhaust emissions of particulate matter from biodiesel are about 47 percent lower than overall particulate matter emissions from diesel.
-
Hydrocarbons: The exhaust emissions of total hydrocarbons are on average 67 percent lower for biodiesel than diesel fuel.
-
Nitrogen Oxides: NOx emissions from pure biodiesel are increased on average by 10 percent. However, some technologies and additives are under development in order to reduce this drawback.
Back to top
Barriers for Further Development
-
Land area: risk of deforestation and competition against food production
-
Engine Manufacturers - Warranties
-
Quality testing costs
-
Exposure to global commodity prices
-
Fluctuating costs
-
Currently more expensive than diesel
-
NOx emissions
-
Large amount of glycerine produced
Back to top
Current Production and Future Potential
The estimated consumption of diesel in the world by the end of 2005 was around 960 billion litres. The production of biodiesel in 2005 worldwide was 4.2 billion litres.
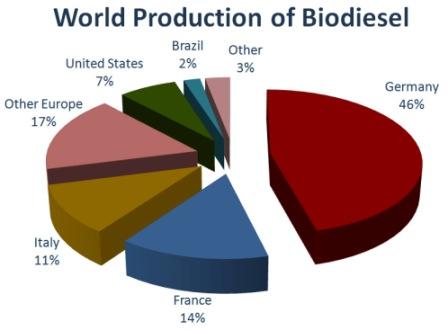
Source: Based on data from the European Biodiesel Board. [13]
 |
| Source: Based on data from the European Biodiesel Board. [13] |
For example, assuming, that 2% of diesel will be substituted by biodiesel,
this would mean an increase of 15 billion of litres in the production of biodiesel.
This boost of biodiesel would have several impacts, including surplus of glycerine,
usage more land area, etc. However, this exercise shows the potential of growth
of biodiesel for the next years.
These impacts and other consequences arising from the increase of production
of biodiesel expected for the next years can be clearly seen in the interactive
tool in this website.