Fuel Cells
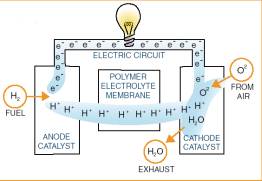
A fuel cell is a device which
combines oxygen and hydrogen electrochemically to produce electricity and
water. Hydrogen is normally produced by reforming natural gas with oxygen and
water to produce hydrogen, carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide. Water is then
added and the carbon monoxide is converted to carbon dioxide and hydrogen. The
carbon dioxide is then removed and the hydrogen is changed by a catalytic
reaction onto its component form which is hydrogen ion (protons) and electrons.
The electrons then flow through a circuit as an electric current thus providing
the power to operate appliances such as a light bulb.† The protons pass through the polymer electrolyte membrane. The
protons and electrons then combine with the oxygen to form the final product
which is ordinary water.
Diagram X
†
The platinum coating on the
cathode catalyses the recombination of protons, electrons and oxygen to
form water. Hydrogen flows into an
anode which is an electrode coated with a platinum catalyst. The platinum
catalyses the splitting of hydrogen into itís component form (protons and
electrons)
![]()
![]() †††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††
††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††††† 
A fuel cell power plant is made
from more than just the fuel cell which is show above. The component part are a
fuel processor, a fuel cell power module, an inverter to convert ac to dc
power, a fuel desulphuriser, an air blower as well as air and fuel pre-heaters.
A fuel cell power plant has the
capability to operate like a CHP plant (combined heat and power) or
cogeneration plant. The ability of the power plant to operate like this will be
highly dependent on the characteristics of the fuel cell as well as the demand
for heat and power. As with conventional CHP plant the ratio of heat to power
is quite high which makes them a good choice for cogeneration applications.
Diagram X

The diagram above shows a typical
outdoor fuel cell power plant.