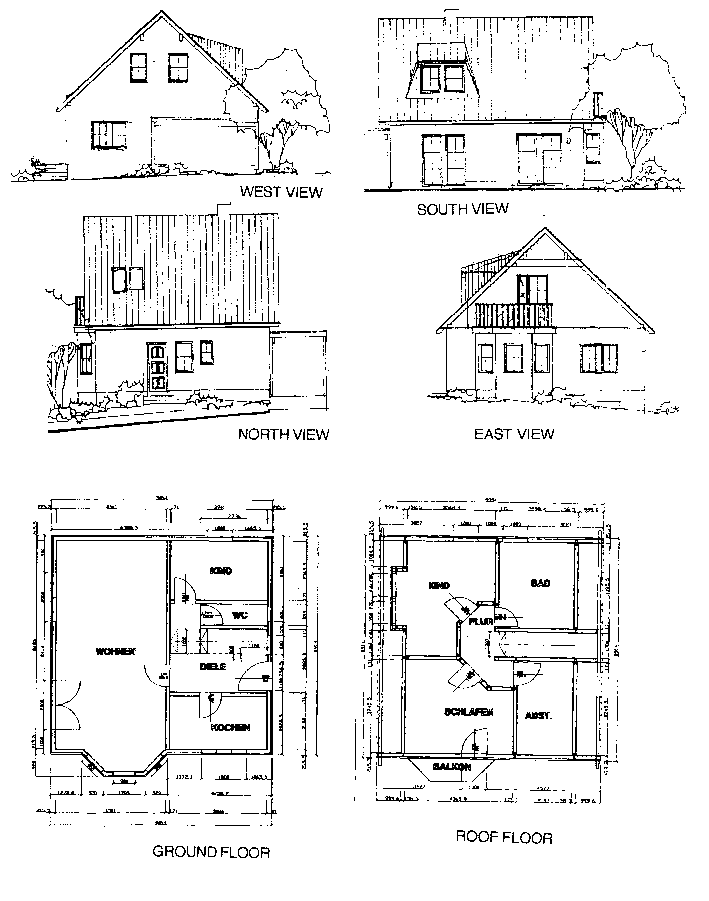
Fig.1: Reference house No.1 "Katarina"
Stefko, J., 1998, Technical university Zvolen, SK
Background
There is a new Standard of Thermal Protection since 1995 in Germany that supposes normative U-values of the opaque and transparent structures - walls, roofs, windows and floors and requires maximal energy consumption of the family houses.
Introduction
Account of the energy consumption includes the energy losses from convection
and infiltration and the energy gains from the solar radiation and from
the casual gains by the form:
Q = 0,9 . (Qt + Qv) - (Qs + Qi) [ kWh/year ]
For determination of the energy losses and gains there are several forms that reach a realistic energy consumption of the building so we can proclaim this standard method as a Simple Simulation Method for the predicting the energy consumption of family houses. The values of energy consumption should be compared with more realistic simulation by ESP-r (see case study 2. - under construction)
Project
All the new project of the family houses built in Germany are required to support by evidence the maximal energy consumption. 90 - 95 % of production of a prefabricated wooden houses made by BUCINA trade (SK) are placed in German market. Technical University Zvolen - Department of Wooden Structures collaborates with BUCINA on the project of wooden family houses. The accounts of the energy consumption of about 50 houses should represent the database which enable the analysis of influences: thermal proprieties, orientation, geometry, portion of transparent structures ... etc.
Task 1: Analyses of the opaque structures on a reference house 1
There were simulated various U-values of walls and windows on
the object of family house "Katarina" (fig. 1)
and the impact to the energy consumption

Fig.1: Reference house No.1 "Katarina"
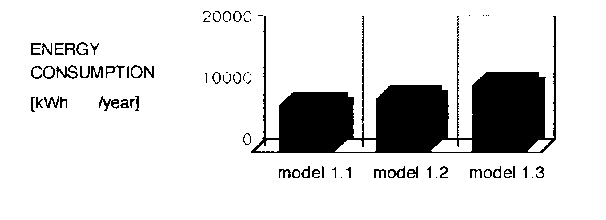
Tab. 1: Energy Consumption of reference house No.1 "Katarina"
| Model No. | U-value of wall
[W/m.K] |
U-value of windows
[W/m.K] |
Energy Consumption By transmission
[kWh/year] |
Energy Consumption
Total [kWh/year] |
Energy Consumption
Total/m3 [kWh/m3.year] |
| 1.1 | 0.22 | 1.3 | 7015.8 | 7587.7 | 18.9 |
| 1.2 | 0.22 | 2.0 | 8480.5 | 8550.5 | 21.2 |
| 1.3 | 0.45 | 2.0 | 10953.7 | 10776.3 | 26.7 |
The analysis was made on the object of double house "ANSA" (fig.2).
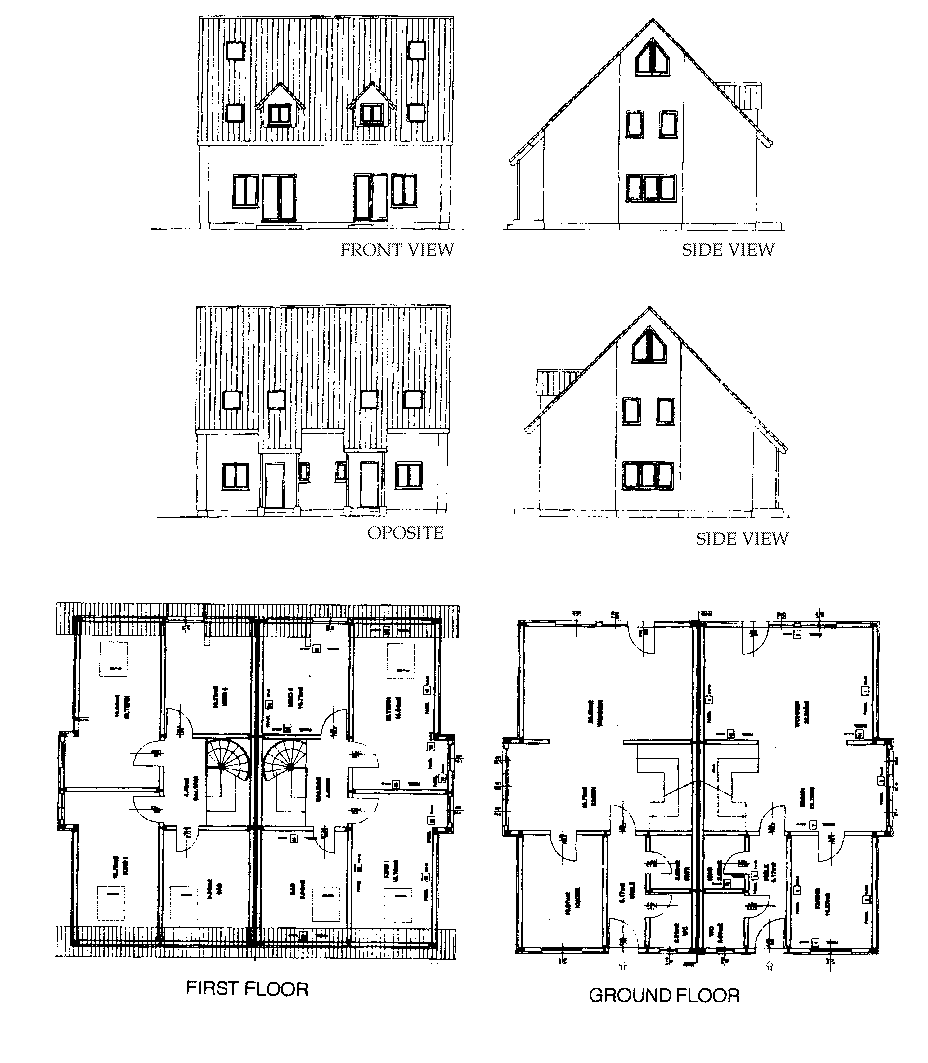
Fig. 2: Reference double house "ANSA"
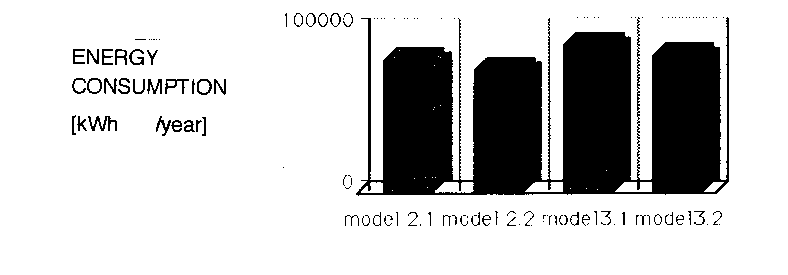
Tab. 2: Energy Consumption of reference house No. 2-3 "ANSA"
| Model No. | Orientation | U-value of windows [W/m.K] | solar gains [kW.h/year] | Energy Consumption
Total [kWh/year] |
Energy Consumption
Total/m3 [kWh/year] |
| 2.1 | north section | 1.5 | 1573.9 | 8241.9 | 19.7 |
| 2.2 | south section | 1.5 | 2322.9 | 7492.9 | 17.9 |
| 3.1 | north section | 2.0 | 1550.0 | 9140.8 | 21.8 |
| 3.2 | south section | 2.0 | 2287.7 | 8403.1 | 20.0 |
Position in the serial layout (middle section, end section and disconnected
end section) was analysed on the reference model No. 4. (fig. 3)
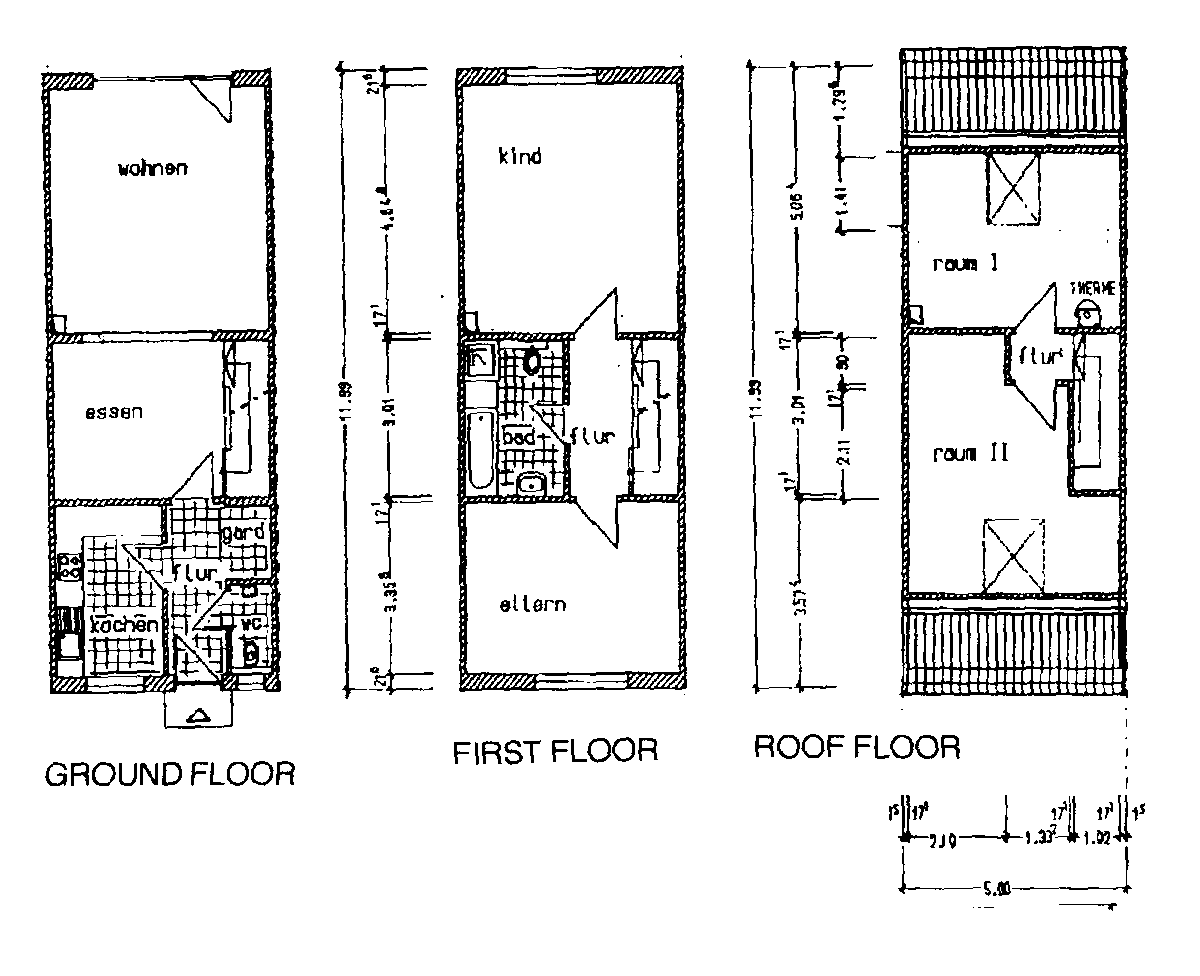
Fig. 3: Reference model of serial building
Tab. 3: Energy Consumption of reference serial house No. 4
| Model No. | Section | U-value of windows
[W/m.K] |
Energy Consumption
Total [kWh/year] |
Energy Consumption
Total/m3 [kWh/year] |
| 4.1 | end match | 1.3 | 8336.6 | 17.66 |
| 4.2 | end disconnected | 1.3 | 9403.2 | 19.84 |
| 4.3 | middle match | 1.3 | 6508.9 | 14.23 |
| 4.4 | middle disconnect. | 1.3 | 7387.9 | 16.14 |
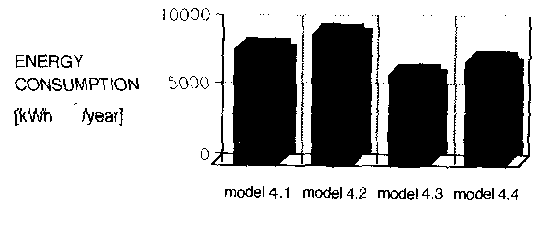
There were simulated the influence of dominant facade orientation (with the majority of transparent areas) and the thermal proprieties of transparent structures on the reference model No. 5 (Fig. 4)
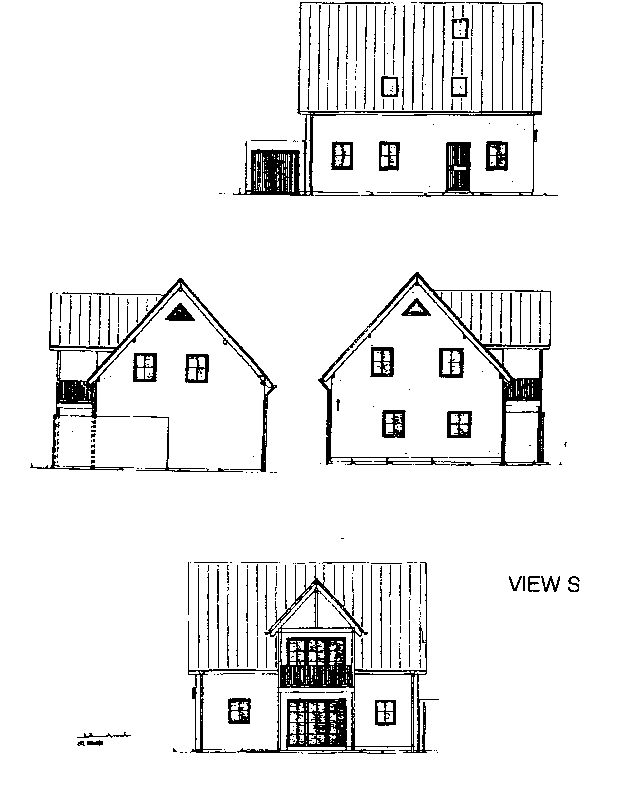
Fig. 4: Reference model No. 5 (the dominant facade below)
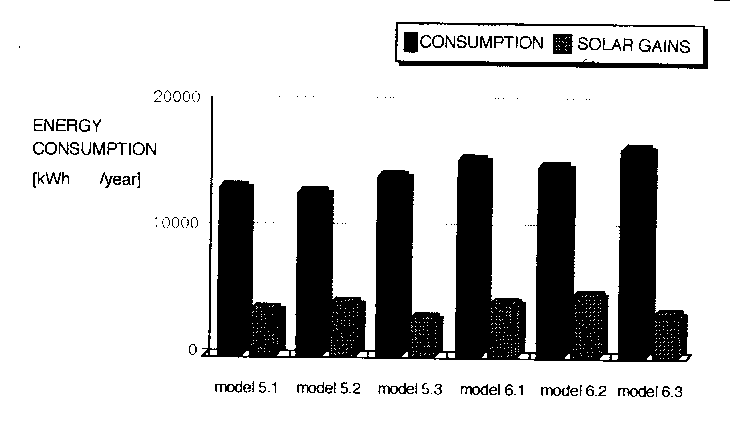
Tab. 4: Energy Consumption of reference house No. 5-6
| Model No. | Orientation of dominant facade | U-value of windows
[W/m.K] |
total energy consumption [kW.h/year] | solar gains [kW.h/year] |
| 5.1 | east | 1.5 | 13270 | 3736 |
| 5.2 | south | 1.5 | 12957 | 4272 |
| 5.3 | north | 1.5 | 14202 | 3027 |
| 6.1 | east | 2.3 | 15592 | 4246 |
| 6.2 | south | 2.3 | 14982 | 4855 |
| 6.3 | north | 2.3 | 16398 | 3493 |
The analysis of energy consumption indicates the influence of
thermal proprieties, orientation and position of family houses. The accounts
of energy consumption enable the wooden family houses to be proclaimed
as "low energy houses". But in the other hand there is the necessity to
investigate the indoor environment quality. This should be realized
only by more realistic simulation methods (for instance
using ESP-r).