

An ESRU Consultancy Case Study
ESRU
Consultancy was commissioned to assess the environmental impact of flue
stacks associated with a new building located in an urban context. The
objective of the study was to evaluate the overall risks of contamination emitted
from 4 roof-top stacks under different wind directions and speeds. CFD
simulations were carried out to account for the 4 cardinal wind directions,
each at two wind speeds (normal and worst case), plus a zero wind speed condition.
The
pictures below show the site where the new building was to be located.
 |
 |
A detailed CFD model was created from an existing AutoCAD model: this included the proposed sand existing buildings as shown in the following image.
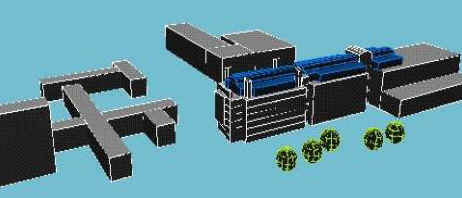 |
The following images show the cut-planes of distributions of wind velocity and concentration of contaminant over the site for a North wind condition.
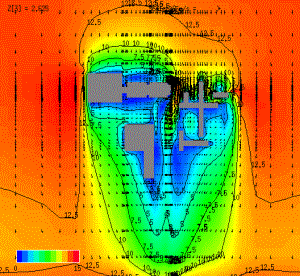 |
 |
The following image shows the coverage of contaminant at 1% of the stack exit
concentration, North wind.
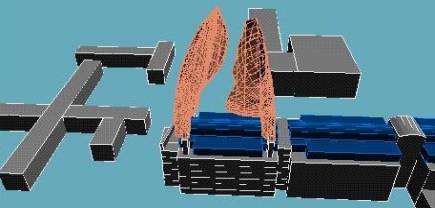 |
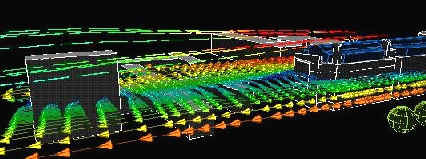
The following images show the air velocity vectors over the site with vector
colour and size indicating the magnitude of the local velocity.
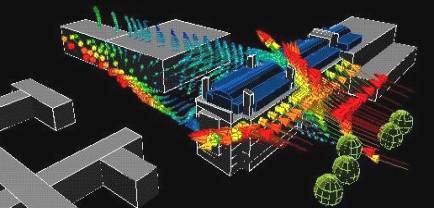 |
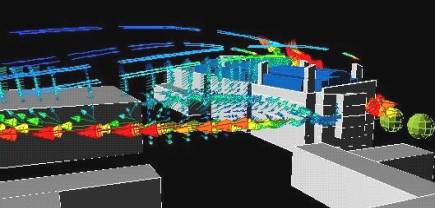 |
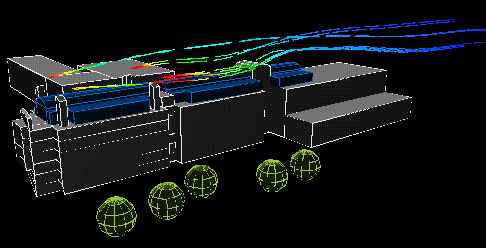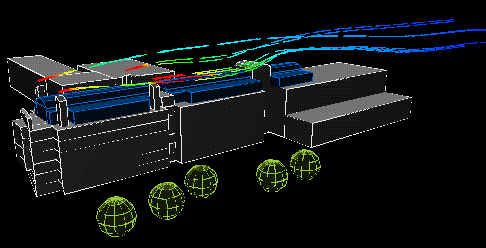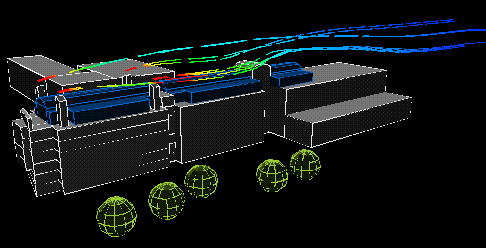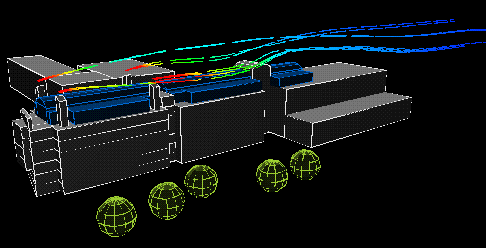
The following animation show the actual flows of the contaminant from different wind directions . The colour variations of the streamlines indicate the concentration of the contaminants along their flow paths; the movement of the streamlines indicate the actual speeds of the plumes emanating from the stacks.
North wind:
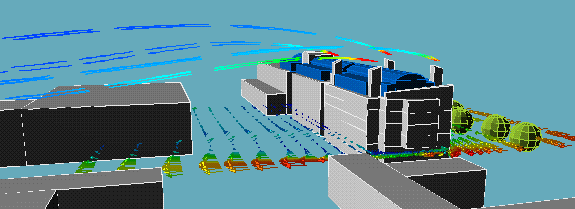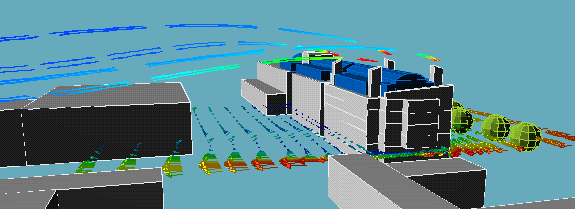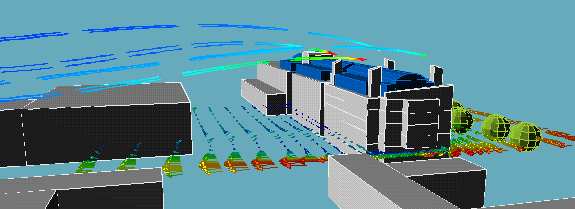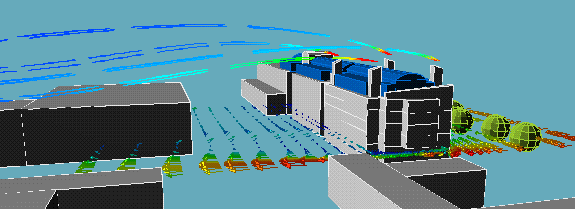 |
South wind:
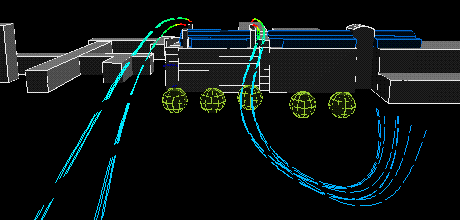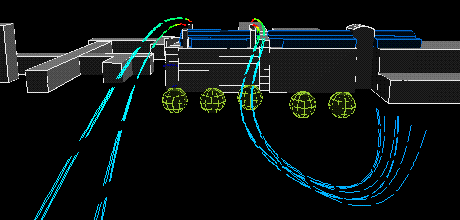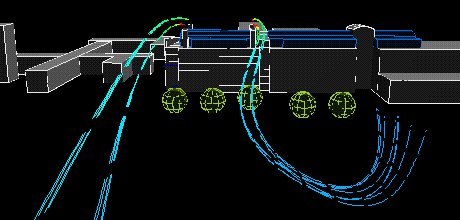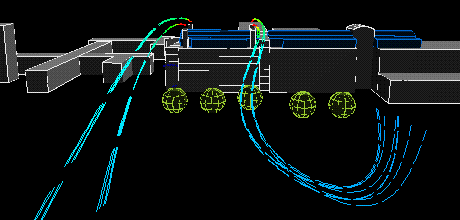 |
West wind:
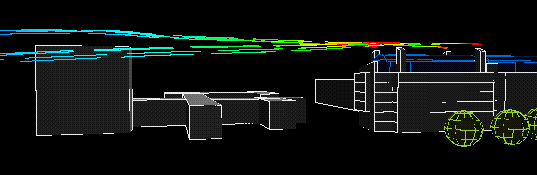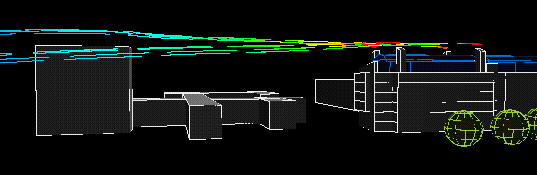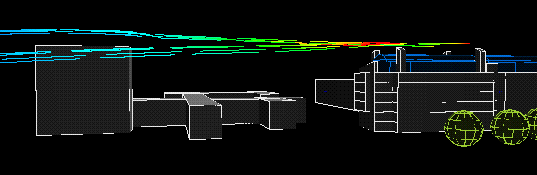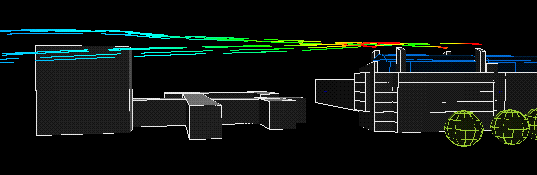 |
East wind:
 |
Some interesting images:
| Air pollution over the car park | Air pollution to an adjacent building |
| Atmosphere of West wind | Atmosphere of East wind |
| Atmosphere of South wind | Air pollution over the roof units |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
The findings: